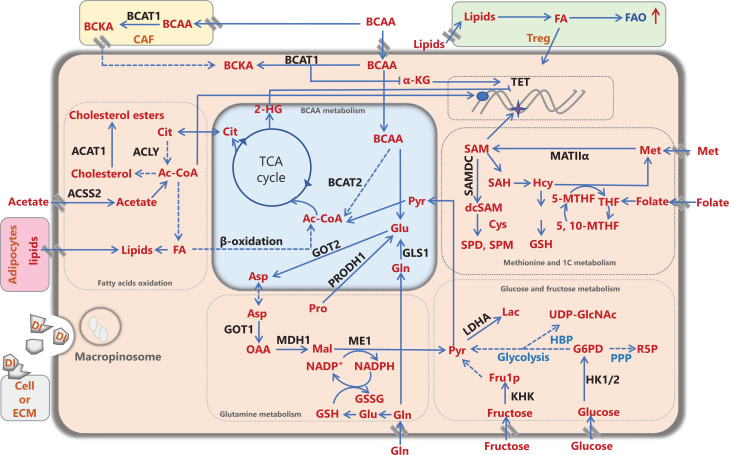
Figure 1.
Metabolic remodeling of cancer cells and the cancer microenvironment. Nutrients and/or intermediate metabolites assimilated from the diet or derived from extracellular matrix molecules or stromal cells in the tumor microenvironment, such as carbohydrates, amino acids, and lipids, are involved in rewiring cancer metabolism to meet energy and biomass synthesis requirements, and support cancer development. Ac-CoA: acetyl-CoA, ACLY: ATP citrate lyase, ACAT1: acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase 1, ACSS2: acetyl-CoA synthetase; Ala: alanine, Asp: aspartate, BCAA: branched-chain amino acid, BCAT1/2: branched-chain amino acid transaminase 1/2, BCKA: branched-chain α-ketoacid, CAF: cancer-associated fibroblast, Cit: citrate, Cys: cysteine, DI: degraded ingredient, FA: fatty acid, FAO: fatty acid oxidation, FASN: fatty acid synthase, Fru1P: fructose-1-phosphate, Gln: glutamine, Glu: glutamate, GLS1: glutaminase 1/glutaminase kidney isoform, mitochondrial, GOT1/2: glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase/aspartate aminotransferase 1/2, G6P: glucose-6-phosphate, GSH: glutathione, GSSG: oxidized glutathione, HBP: hexosamine biosynthetic pathway, Hcy: homocysteine, 2-HG: 2-hydroxyglutarate, HK1/2: hexokinase 1/2, α-KG: α-ketoglutarate, KHK: ketohexokinase, Lac: lactate, LDHA: lactate dehydrogenase A, Mal: malate, ME1: NADP-dependent malic enzyme 1, Met: methionine, MAT IIα: methionine adenosyltransferase IIα, MDH1: malate dehydrogenase 1, NADP+: nicotinamide-adenine-dinucleotide phosphate, NADPH: reduced NADP, OAA: oxaloacetate, PPP: pentose phosphate pathway, Pro: proline, PRODH1: proline dehydrogenase, Pyr: pyruvate, R5P: ribose-5-phosphate, SAH: S-adenosylhomocysteine, (dc) SAM: (decarboxylated) S-adenosylmethionine, SAMDC: S-adenosylmethionine decarboxylase, SPD: spermidine, SPM: spermine, TCA: tricarboxylic acid cycle, TET: ten-eleven translocation, THF: tetrahydrofolate, 5-MTHF: 5-methyltetrahydrofolate, 5,10-MTHF: 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate, Treg: regulatory T cell, UDP-GlcNAc: UDP-N-acetylglucosamine.