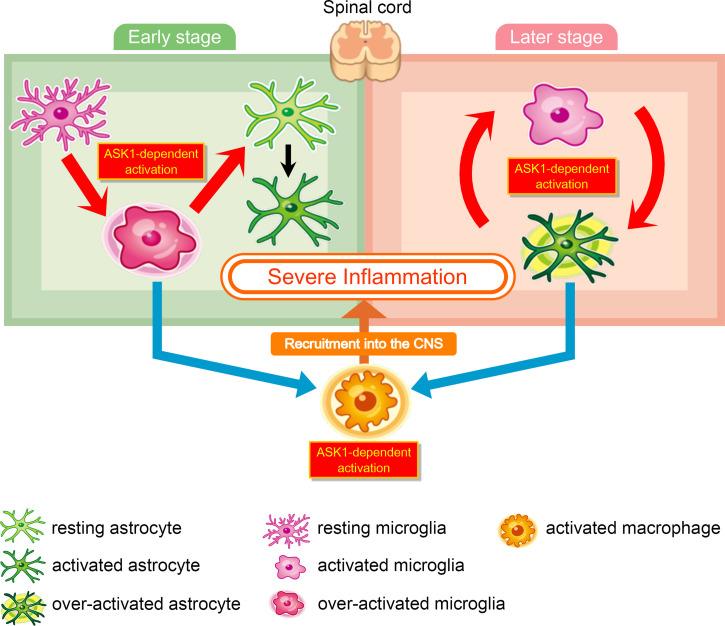
Fig. 7.
Schematic model of ASK1-mediated glial interaction during neuroinflammation. (Left) ASK1 signaling in microglia plays a pathogenic role in the early stage of EAE: ASK1 signaling in microglia polarizes microglia toward a proinflammatory state (red arrow). Proinflammatory microglia induce proinflammatory astrocytes (red arrow), produce CCL2 (blue arrow), and recruit macrophages into the CNS (orange arrow). ASK1 signaling in macrophages promotes macrophages to be in a proinflammatory state. ASK1-mediated activation of these glial cells causes severe inflammation. (Right) ASK1 signaling in astrocytes plays a pathogenic role in the later stage of EAE: ASK1 signaling in astrocytes promotes secretion of cytokines and chemokines to induce proinflammatory microglia and recruit macrophages into the CNS. Proinflammatory microglia induce proinflammatory astrocytes; and therefore we propose a glial interaction cycle, in which astrocytes and microglia activate each other in an ASK1-dependent manner. ASK1-mediated activation of these glial cells causes sustained inflammation.