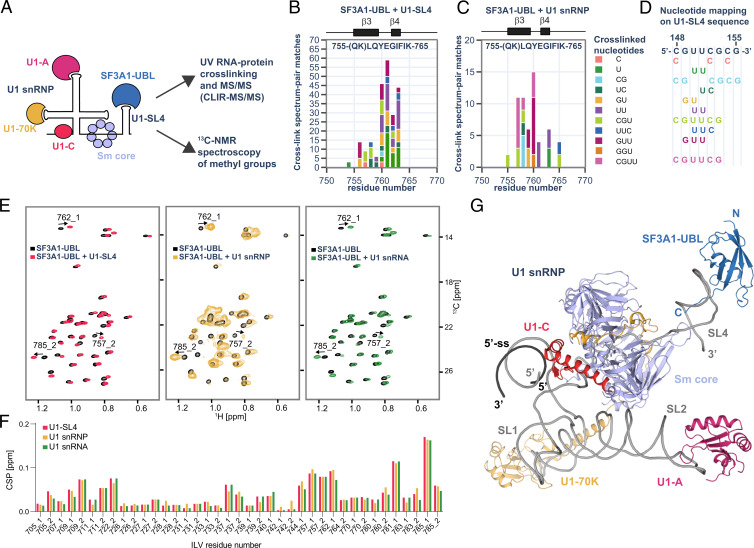
Fig. 4.
Analysis of SF3A1-UBL binding to U1 snRNP. (A) Schematic representation of the SF3A1-UBL/U1 snRNP complex analysis. (B) Protein–RNA cross-links identified for 1:1 complex of SF3A1-UBL and U1-SL4 by CLIR-MS/MS plotted on the sequence of SF3A1-UBL. The bar colors represent the nucleotide composition of the RNA adducts. Protein–RNA cross-links are shown as counts of cross-link spectrum matches. (C) Cross-links identified for SF3A1-UBL bound to in vitro–reconstituted U1 snRNP. (D) Mapping of nucleotides cross-linked to SF3A1-UBL on the sequence of U1-SL4. (E) Overlay of the 2D 1H-13C HMQC spectra of the free SF3A1-UBL protein (black) and in complex with U1-SL4 (red), U1 snRNP (yellow), and U1 snRNA (green). (F) Plot showing the CSPs of the methyl groups of isoleucine, leucine, and valine (ILV) of SF3A1-UBL observed upon addition of U1-SL4 (red), U1 snRNP (yellow), or U1 snRNA (green). Methyl groups are labeled according to the residue number; 1 or 2 stands for HD1/CD1 and HD2/CD2 in the case of leucine or HG1/CG1 and HG2/CG2 in the case of valine. (G) Structural model of SF3A1-UBL bound to U1 snRNP.