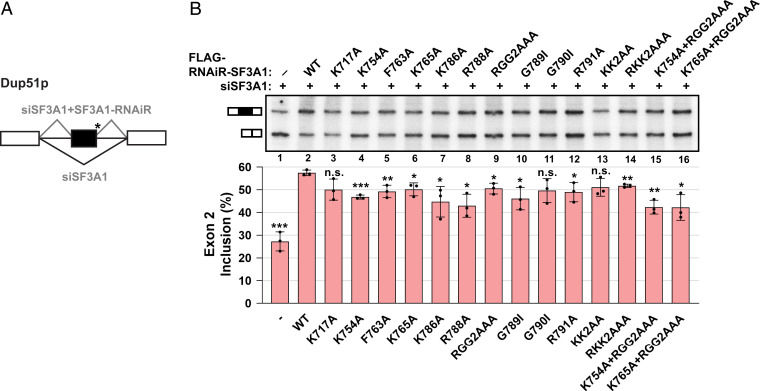
Fig. 5.
Mutations in SF3A1-UBL interfere with splicing rescue of the Dup51p minigene reporter under SF3A1 knockdown conditions. (A) Schematic representation of three-exon/two-intron Dup51p reporters depicting the splicing pattern upon siRNA-mediated knockdown and rescue with an siRNA-resistant construct. The asterisk indicates a mutant 5′-ss. (B) Primer extension analysis monitors the inclusion of exon 2 in RNA isoforms of the Dup51p minigene reporter. The mRNA products are shown schematically to the left of the gel image. All cells were transfected with siSF3A1 and plasmid harboring WT or mutant FLAG-RNAiR (RNA interference-resistant)-SF3A1. In the absence of the RNAi-resistant clone, exon 2 inclusion is inhibited (lane 1). Cotransfection with the WT RNAi-resistant SF3A1 clone rescues exon 2 inclusion under siSF3A1 treatment (lane 2), which is reduced if splicing rescue is performed using mutant RNAi-resistant SF3A1 (lanes 3 to 16). Percent exon 2 inclusion (n =3; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001) is plotted below the gel.