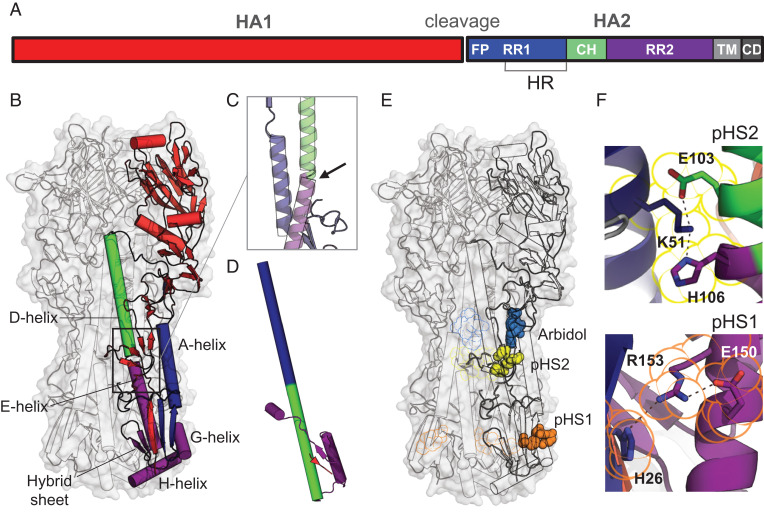
Fig. 1.
Influenza HA protein structure. (A) Schematic representation of HA with indicated fusion peptide (FP), refolding regions 1 and 2 (RR1 and RR2), heptad repeat (HR) motif, central helix (CH), transmembrane (TM) domain, and cytoplasmic domain (CD). (B) Structure of prefusion trimeric WT H3-HK68 [PDB identifier 4FNK (22)] in surface representation (gray). The internal protein structure is outlined in the cartoon with one monomer colored according to A. (C) Bend of the helical structure between helices D and E. (D) Conformation of the postfusion monomer [PDB identifier 1QU1 (50)]. (E) Location of histidine switches 1 and 2 (pHS1 and pHS2). The histidines and charged residues forming the switches are shown in space, filling representation in orange for pH switch 1 (pHS1) and yellow for pH switch 2 (pHS2). Fusion inhibitor Arbidol is plotted in blue based on PDB identifier 5T6N (18). pHS1, pHS2, and Arbidol binding to the other protomers were plotted as outline. (F) Details of the structure of the histidine switches pHS1 and pHS2 in the WT HA. H106-K51-E103 linked by hydrogen bonds in pHS2 (Top) and H26-R153-E150 triad in pHS1 (Bottom). Residues belonging to pHS1 and pHS2 are outlined in the same color as in E.