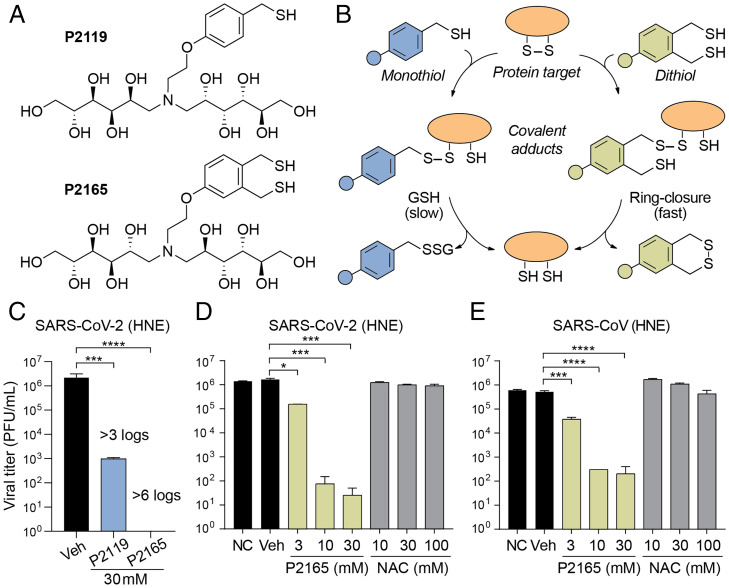
Fig. 1.
Thiol-based reducing agents have potent virucidal activity against human coronaviruses. (A) Chemical structures of P2119 and P2165 reducing agents. (B) Mechanisms of disulfide reduction by thiol-based reducing agents. Adducts formed with P2119 require a second thiol equivalent (e.g., from GSH or drug) to resolve the mixed disulfide, whereas the adduct formed with P2165 rapidly undergo intramolecular thiol-disulfide exchange. (C–E) Comparison of 72-h titers between nontreated control (NC), PBS vehicle (Veh), or reducing agents-treated SARS-CoV or SARS-CoV-2 infected primary HNE cultures at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 0.1. Triplicated titers of the virus in cultures from the same donor were analyzed by ANOVA with Dunnett’s test. *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001.