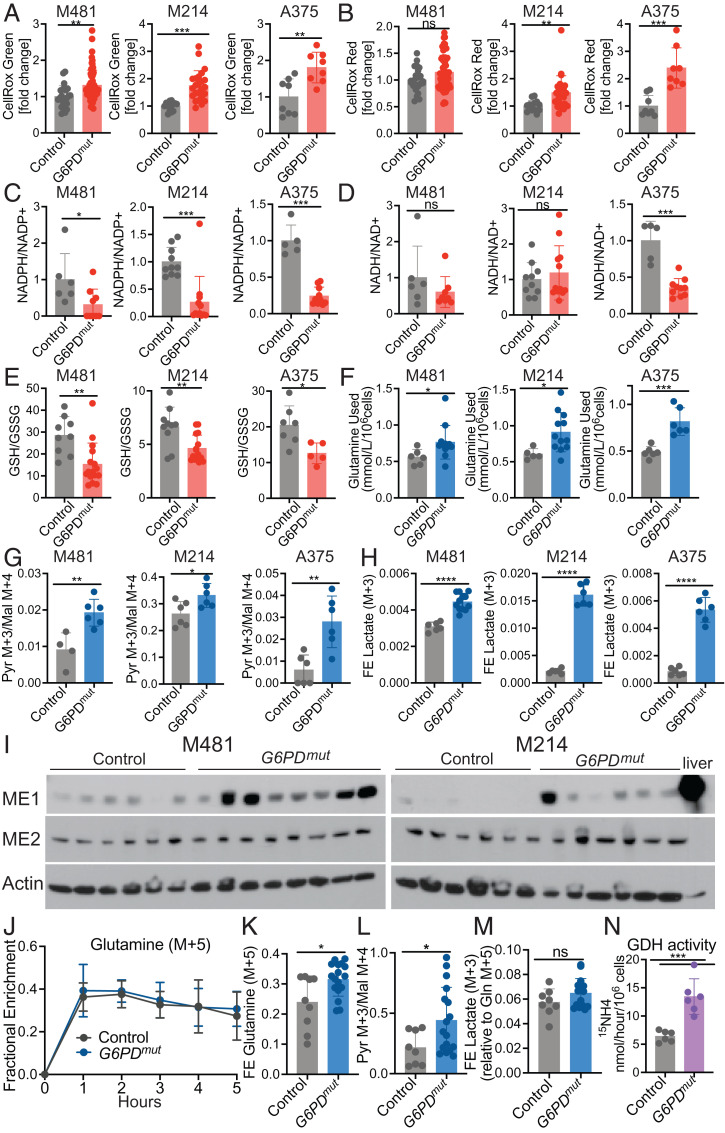
Fig. 4.
Reduced G6PD function induces oxidative stress and increases glutamine utilization. (A and B) ROS levels based on median fluorescence intensity of CellRox green (A) or CellRox red (B) in subcutaneous tumors formed by G6PD mutant or control melanoma cells (n = 2 to 3 clones per genotype per melanoma with five mice per clone in two to three independent experiments per melanoma). Each dot represents data from one mouse. (C–E) The relative ratios of NADPH to NADP+ (C), NADH to NAD+ (D), and the absolute molar ratios of GSH to GSSG quantified with an internal standard (E) in G6PD mutant or control M481, M214, and A375 melanoma cells (three independent experiments were performed per melanoma and one representative experiment per melanoma is shown; n = 5 to 15 mice per group). (F) The amount of glutamine consumed from the culture medium is shown as mmol/L/106 cells for G6PD mutant and control melanomas after 24 (M481 and M214) or 8 h (A375) in culture (n = 2 clones per genotype per melanoma, with three to six replicate cultures per clone in two independent experiments per melanoma). (G and H) G6PD mutant or control melanoma cells were cultured with [U-13C] glutamine and the ratio of pyruvate (m+3) to malate (m+4) (G) and fractional enrichment in lactate (m+3) were measured (H) (n = 2 clones per genotype per melanoma, with six replicate cultures per clone; one representative experiment is shown from two to three independent experiments per melanoma). (I) Western blot analysis of ME1 and ME2 in lysates of subcutaneous tumors. Actin is a loading control. Each lane is a different tumor from a different mouse. Normal mouse liver is shown as a positive control. (J–M) NSG mice xenografted with G6PD mutant or control M481 melanoma cells were infused with [U-13C] glutamine. The fractional enrichment of glutamine m+5 in the blood (J) and in subcutaneous tumors after 5 h of infusion (K). The ratio of pyruvate (m+3) to malate (m+4) (L) and fractional enrichment of lactate (m+3) normalized to the fractional enrichment of glutamine (m+5) (M) (n = 2 clones per genotype per melanoma, with four to eight mice per clone in two independent experiments). Each dot represents a different tumor in a different mouse. (N) G6PD mutant and control melanoma cells were cultured in medium supplemented with L-[α-15N]glutamine and GDH activity was measured based on the rate at which 15N was transferred from glutamine to 15NH4 (two clones per genotype from three independent experiments; each dot represents cells from a different culture; n = 3 wells per clone). Data represent mean ± SD. Statistical significance was assessed using Mann–Whitney U tests (A–C, J, and M), Student’s t tests on log2-transformed data (D–F), Student’s t tests (G, H, and K–M), Welch's t test (H), or Student’s t tests on log2-transformed data (N). Statistical tests were two-sided. Multiple comparisons were adjusted by the FDR method: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001, ns = not significant.