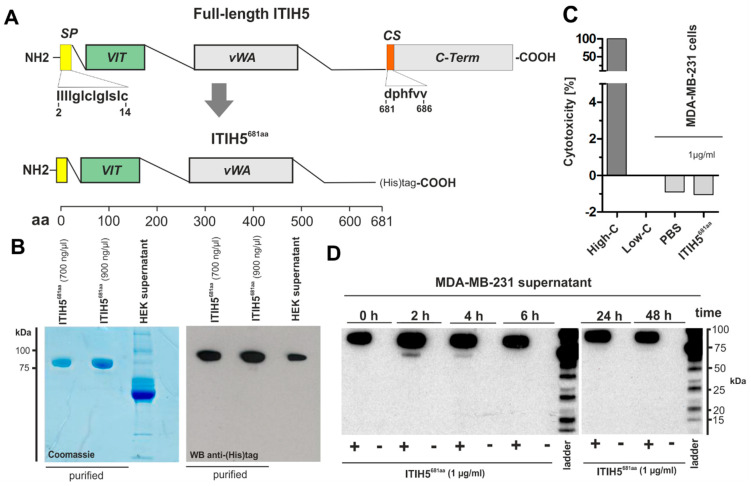
Figure 2.
In Vitro synthesis, toxicity, stability, and specificity of recombinant N-terminal ITIH5t polypeptides. (A) Schematic drawing of the full-length ITIH5 protein (942 aa) and the derived N-terminal ITIH5t protein (681 aa), which includes both the VIT (relative aa position according to specific databases: PFAM = 51–159; Prosite profiles = 35–161) and vWA (relative aa position: PFAM = 295–466; Prosite profiles = 295–478) domains. (B) Visualization of the recombinantly produced N-terminal ITIH5t polypeptide after purification by using Coomassie staining and Western blotting. Immunodetection was performed using a His-tag antibody. (C) A LDH cytotoxicity assay was performed. The recombinant N-terminal ITIH5t did not show any toxicity. (D) The biochemical stability of N-terminal ITIH5t applied to the supernatant of aggressive MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells showed an undiminished peptide concentration, which could be re-isolated over a period of 48 h.