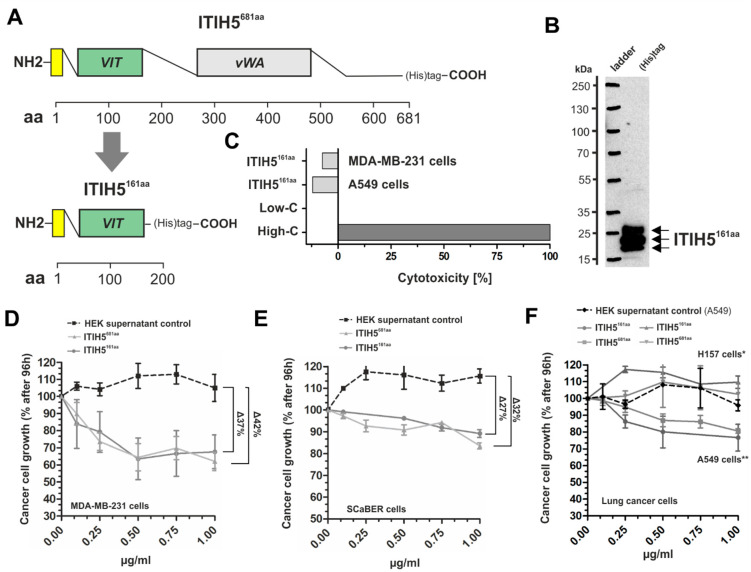
Figure 4.
Tumor-suppressive impact of the recombinant VIT-domain containing polypeptide (ITIH5161aa) derived from the N-terminal ITIH5t protein applied to breast, bladder and lung cancer cells. (A) Schematic drawing of the N-terminal ITIH5681aa polypeptide (681 aa) and the truncated ITIH5161aa polypeptide (161 aa) covering the VIT domain. (B) Visualization of the recombinant ITIH5161aa produced after purification using immuno-detection via a His-tagged antibody. (C) A LDH cytotoxicity assay was performed using breast and lung cancer cells. The recombinant ITIH5161aa did not show any non-specific cytotoxicity. (D–F) In vitro dose–response curve analysis confirmed the concentration-dependent growth inhibition (27–42%) that was similar to treatment with either ITIH5681aa or ITIH5161aa polypetides for 96 h in (D) aggressive breast cancer cells (MDA-MB-231) and (E) squamous basal bladder cancer cells (SCaBER). (F) Specific growth inhibition was confirmed in lung adenocarcinoma cells (A549), whereas squamous lung cancer cells (H157) did not respond to either of the truncated ITIH5 polypeptides. Note: Purified scrambled proteins (processed in a similar manner to the truncated ITIH5 proteins) of the supernatant of the host HEK cells originally used for in vitro production of the recombinant truncated ITIH5 proteins showed no growth-inhibitory effects. Treated cells were normalized to the scrambled controls, since HEK proteins increase cell growth rates.