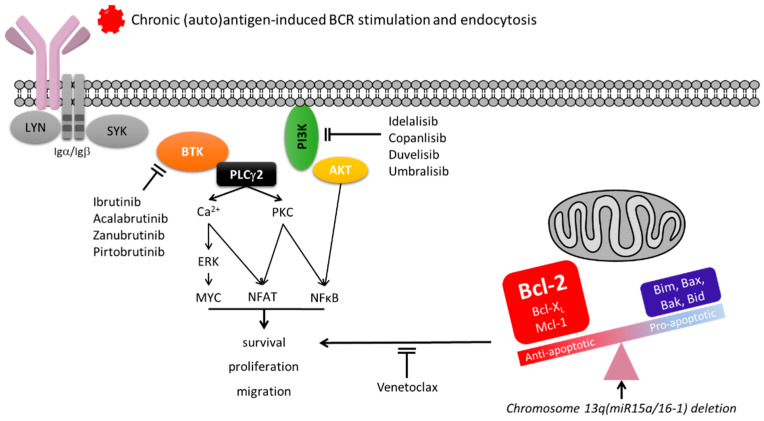
Figure 2.
Simplified diagram of BCR signaling and therapeutic targeting in CLL. BCR engagement by (auto)antigen leads to the proximal activation of a complex of kinases and scaffold proteins, initiating with the phosphorylation of the immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motifs (ITAMs) in the C-terminal tail of BCR-associated Igα/CD79a and Igβ/CD79b by LYN. Phosphorylated ITAMs leads to SYK recruitment and propagation of signal to Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) and phospholipase Cγ2 (PLCγ2). LYN-dependent phosphorylation of the cytoplasmic domain of CD19 also recruits phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K). Activation of a network of distal signaling molecules follows. Activation of PLCγ2 leads to the release of intracellular Ca2+ and activates protein kinase C (PKC). PKC subsequently induces the activation of transcription factors, including NF-κB and nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT). Recruitment of PI3K to the plasma membrane leads to optimal activation of BTK and AKT. PLCγ2 is also involved in the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways, including the extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK). The third phase of events involves modulation of multiple downstream regulators, which ultimately mediate changes in cell proliferation, survival, and migration, via both phosphorylation and transcriptional modulation of key regulators of cell survival (e.g., Mcl-1, Bim). In CLL, strength of BCR signal, which is controlled by surface IgM levels, will determine cell fate with a balance towards anergy particularly when sIgM levels are low. MiR15a/16-1 deletion at chromosome 13, allowing overexpression of antiapoptotic Bcl-2 protein favoring survival, counter the proapoptotic mechanisms associated with anergy. Therapeutical inhibition of BTK variably blocks BCR signaling in CLL depending, amongst other factors, on sIgM levels and signal strength. Addition of PI3K inhibitors may fully suppress the residual signaling activity. BH3 mimetics (venetoclax) block the antiapoptotic mechanisms resulting from Bcl-2 overexpression found in CLL.