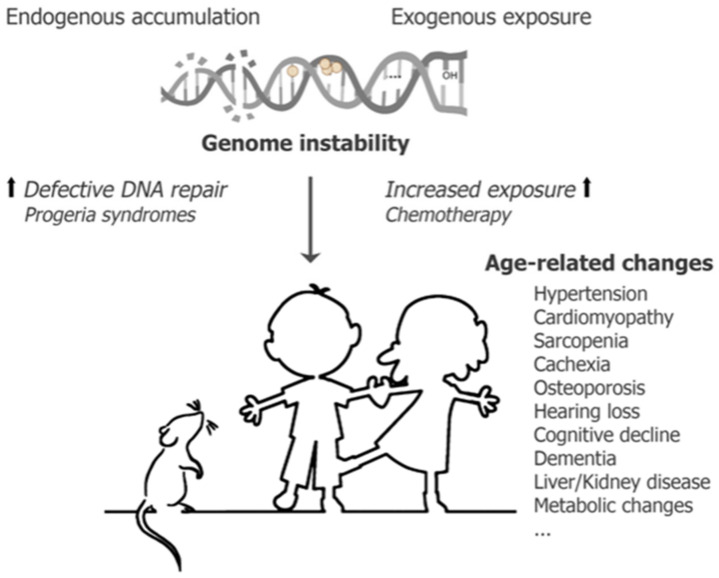
Figure 3.
Genome instability induces premature aging. Persisting DNA damage, originating from both endogenous and exogenous sources, normally results in the onset of aging pathologies. These consequences are accelerated either when DNA repair processes are defective, in the case of progeria syndromes and thus more endogenous lesions persist, or when exogenous exposure is increased as during chemotherapy treatment.