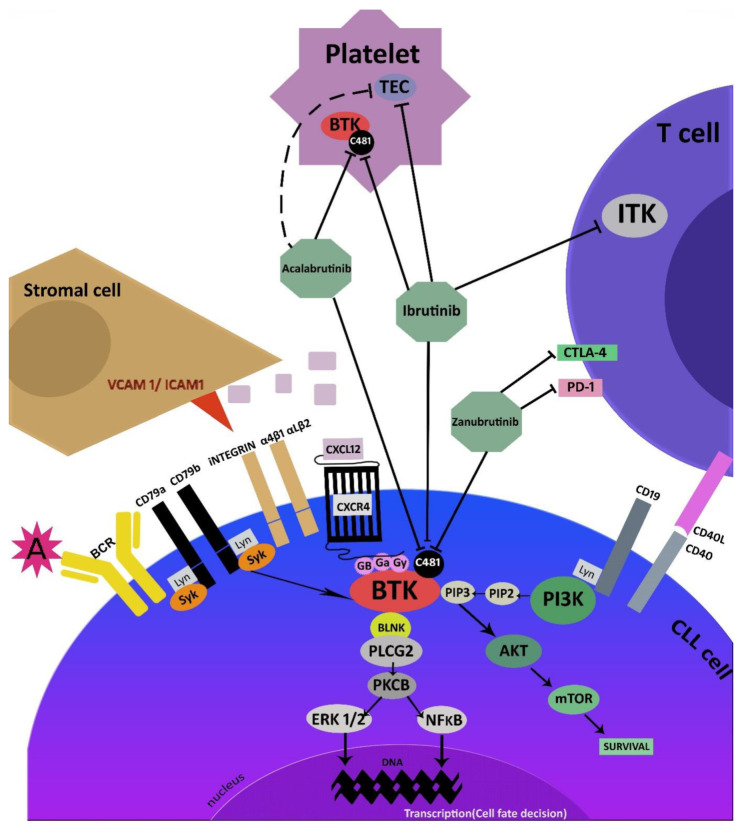
Figure 1.
Signaling pathways involved in the mechanisms of action of Bruton kinase inhibitors in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) cells. Abbreviations: AKT—protein kinase B, BCR—B-cell receptor, BLNK—B-cell linker protein Btk: Bruton’s tyrosine kinase, CTLA-4: cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen-4, C481—cysteine residue, CXCL12—C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 12, CXCR4—C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4, EGFR: epidermal growth factor receptor, ERK1/2—extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2, Gα, G β, Gϓ: G protein subunits, ITK—IL2-inducible T-cell kinase, Lyn—member of the Src kinase family, NFkB—nuclear factor kappa B, PI3K—phosphoinositide 3-kinase, PLCG2—phospholipase gamma 2, PKCB—protein kinase C beta, PKCB: protein kinase C beta, PD-1—programmed death-ligand 1, PIP1, PIP2—phosphatidylinositols 1 and 2, Syk—spleen tyrosine kinase, TEC—tyrosine kinase expressed in hepatocellular carcinoma.