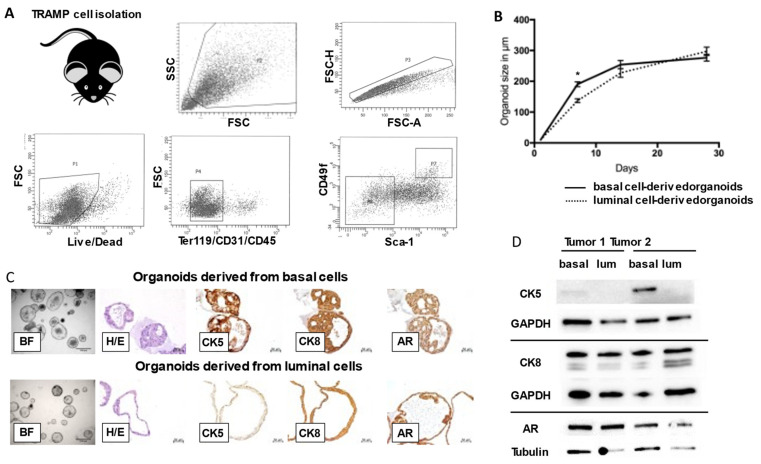
Figure 1.
Establishment of basal cell-derived and luminal cell-derived organoid lines from TRAMP tumors. (A) Representative gating strategy for primary TRAMP tumor single cell suspension staining and sorting. Cells were sorted according to LIVE/DEAD yellow staining, negative blood lineage marker staining, and basal cell markers expression (Sca-1/CD49f), as previously published by our group [23]. (B) Basal cell-derived organoids and luminal cell-derived organoids exhibit no significant differences in maximum organoid size, although basal cell-derived organoids grow relatively faster within week one after plating. (C) Representative brightfield, hematoxylin/eosin, and immunohistochemistry analyses of TRAMP tumor cell-derived organoids shows differences in cellular architecture and protein expression between organoids of basal and luminal origin. Interestingly, basal cells isolated from TRAMP tumors gave rise to multilayered organoids strongly expressing the basal cell marker CK5 as well as CK8 and AR (upper panel), while luminal cell-derived organoids mainly grew as monolayered organoids not expressing CK5 (lower panel). Scale bars represent 50 µm. (D) Immunoblotting experiments of basal and luminal-cell derived organoid lines derived from two individual TRAMP tumors show relatively higher expression of CK5 in basal cell-derived organoids (basal) when compared to luminal cell-derived organoids (lum). No differences between organoid origins are seen in expression of the luminal cytokeratin CK8 or the androgen receptor (AR). Original Western blot can be found in File S1.