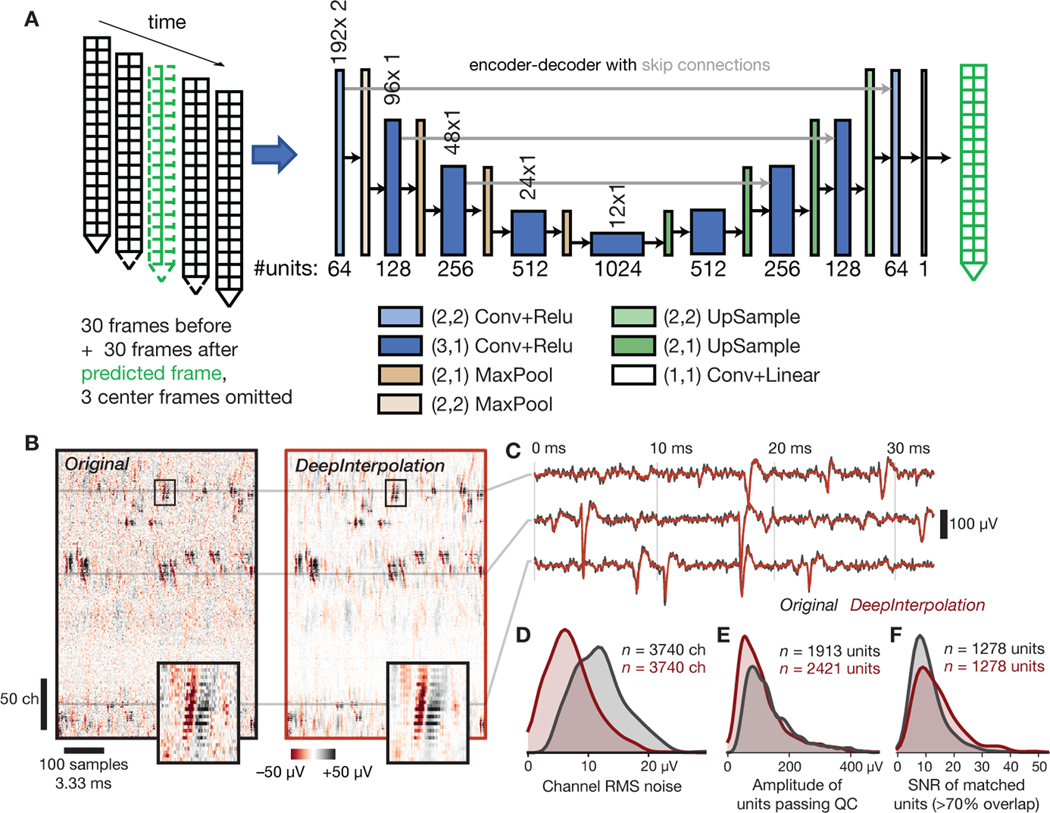
Fig. 4 |. Applying DeepInterpolation to electrophysiological recordings decreases background noise and yields additional detected neuronal units.
(A) Structure of the DeepInterpolation encoder-decoder network for electrophysiological data recorded from a Neuropixels silicon probe, with two columns of 192 electrodes each, spaced 20 μm apart. Data is acquired at 30 kHz. (B) Side-by-side comparison of original (left) and denoised (right) data, plotted as a 2D heatmap with time on the horizontal axis and channels along the vertical axis. Insets show a close-up of a single action potential across 22 contiguous channels (the box is 3.6 ms wide). (C) Denoised time series (red) overlaid on the original time series (gray) for three channels from panel B. (D) Histogram of RMS noise for all channels from 10 experiments, before and after applying DeepInterpolation. (E) Histogram of waveform amplitudes for all high-quality units from 10 experiments. (F) Histogram of waveform SNRs for all units that were matched before and after denoising.