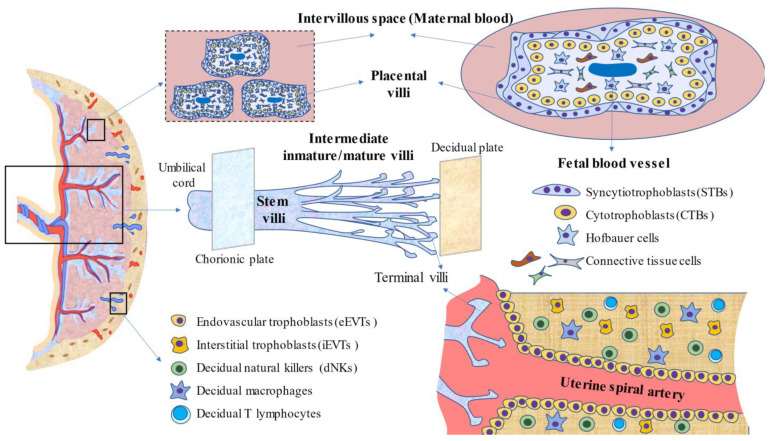
Figure 1.
An integrative picture of the components of the placenta. Herein, the main cell types and structures formed are summarized. At the top, placental villi and their cells, as well as the location of the maternal and fetal blood, in the intervillous space and inside the villi, respectively, are represented. In the center of the image, the villous tree, as well as the different types of villi, are represented. The chorionic plate, or fetal surface, is covered by the amnion, where the umbilical cord is attached. The decidual basal plate or maternal surface is in contact with the endometrium. As represented at the bottom, profound remodeling of the uterine spiral arteries is mainly due to the coordinated efforts of a set of cells, mainly extravillous trophoblasts (EVTs) and immune cells, prominently represented by decidual natural killers (dNKs). Having complete knowledge of the placenta in non-pathologic pregnancies is crucial for the study of different pregnancy complications, as the placenta is responsible for a wide variety of functions, as is subsequently discussed.