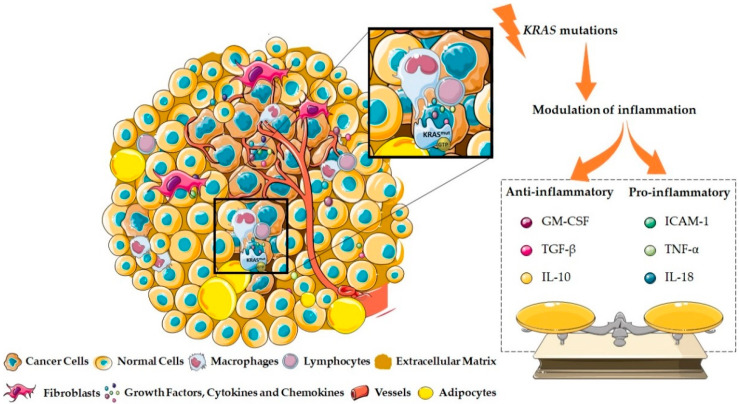
Figure 2.
KRAS as a crucial TME modulator. The TME is composed, not only of tumor cells, but also several non-tumor stromal elements such as immune cells, fibroblasts, adipocytes, endothelial cells, neurons, osteoblasts, osteoclasts, and ECM components. This dynamic, challenging microenvironment modulates and can be modulated by several factors, namely, KRAS mutations. Several studies have reported that KRAS mutations can drive the secretion of anti-inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-10, TGF-β, and GM-CSF, with the ability to sustain an immunosuppressive TME and to promote tumor progression. Other studies have also demonstrated that KRAS mutations may interfere with the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines, with an anti-tumor effect, such as ICAM-1, TNF-α, and IL-18. Thus, KRAS seems to act as a modulator of both an anti-inflammatory and a pro-inflammatory TME.