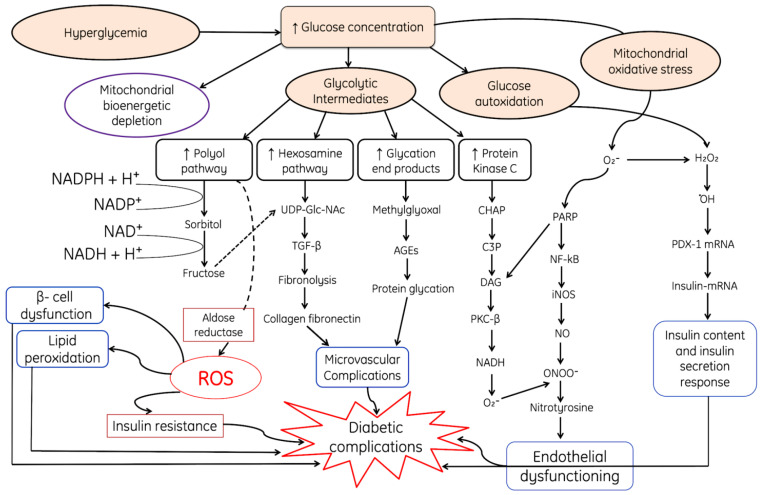
Figure 4.
Hyperglycemic condition is one of the major sources of ROS and leads to modulation of various metabolic downregulatory pathways. Increased glucose results in auto-oxidation and production of H2O2, ·OH and activation of downregulatory pathways such as PDX-1 and insulin-(mRNA) and increases the secretion, where DAG: Diacyl glycerol, PKC-β: Protein kinase-beta, NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa light chain enhancer of activated B cells, AGEs: Advanced glycated end products, UDP-Glac-NAc: Uridine diphosphate N-acetylglucosamine, TGF-β; Transforming growth factor beta, PDX1; pancreatic and duodenal homeobox-1, PARP: Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase. Closure of K+-ATP-dependent channels results in membrane depolarization and activation of voltage-dependent calcium channels, leading to an increase in intracellular calcium concentration; this triggers pulsatile insulin secretion. Note: Upward arrows indicate increase and downward arrows indicate decrease.