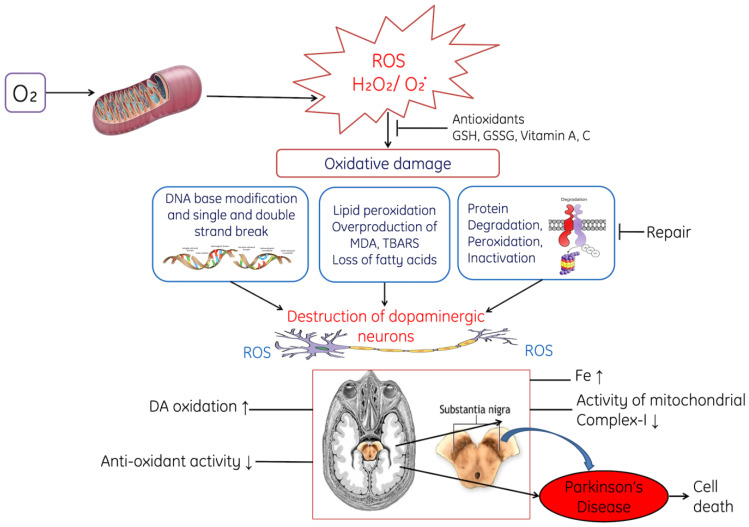
Figure 8.
The diagram shows the role of ROS in Parkinson’s disease through the of dopaminergic neurons. ROS exerts oxidative stress on DNA leads to modification in base and causes fragmentation in DNA. Peroxidative damage in lipids, loss of fatty acids, changes in plasma membrane and degradation of proteins. All these changes damage the dopaminergic neurons, where H2O2: Hydrogen peroxide; ROS: Reactive oxygen species, GSH: Reduced glutathione, GSSG: Oxidized glutathione.