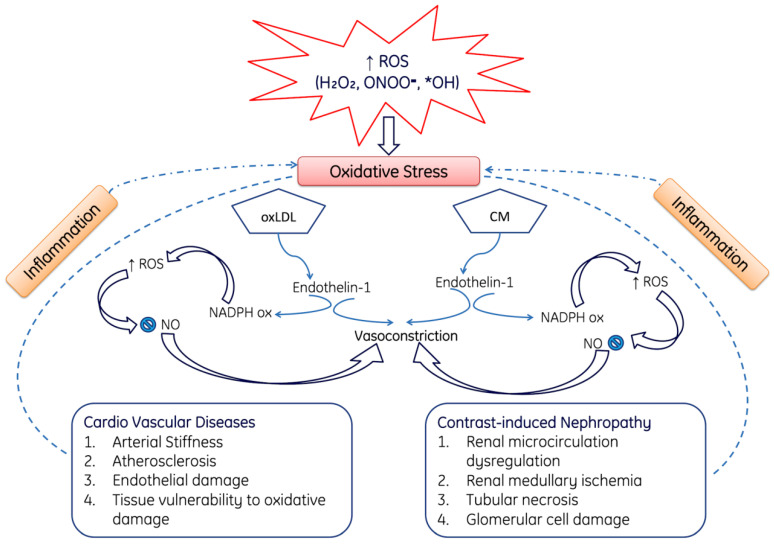
Figure 9.
This diagram represents the role of ROS in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular cardiovascular diseases and contrast-induced nephropathy. Over produced reactive oxygen species such as H2O2, ONOO−, *OH induces oxidative damage on lipids (OxLDL) and CM and leads in the production of Endothelin-1. Endothelin-1along with ROS-mediated inflammation causes arterial stiffness, atherosclerosis, endothelial damage, tissue injury. Among the renal complications it causes renal microcirculation dysfunction, renal medullary ischemia, tubular necrosis and damages glomerular injury. Were, OxLDL: Oxidized low-density lipoproteins, CM: Cell membrane, NO: Nitric oxide, NADPH ox: nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase. Note: Upward arrows indicate increase and downward arrows indicate decrease.