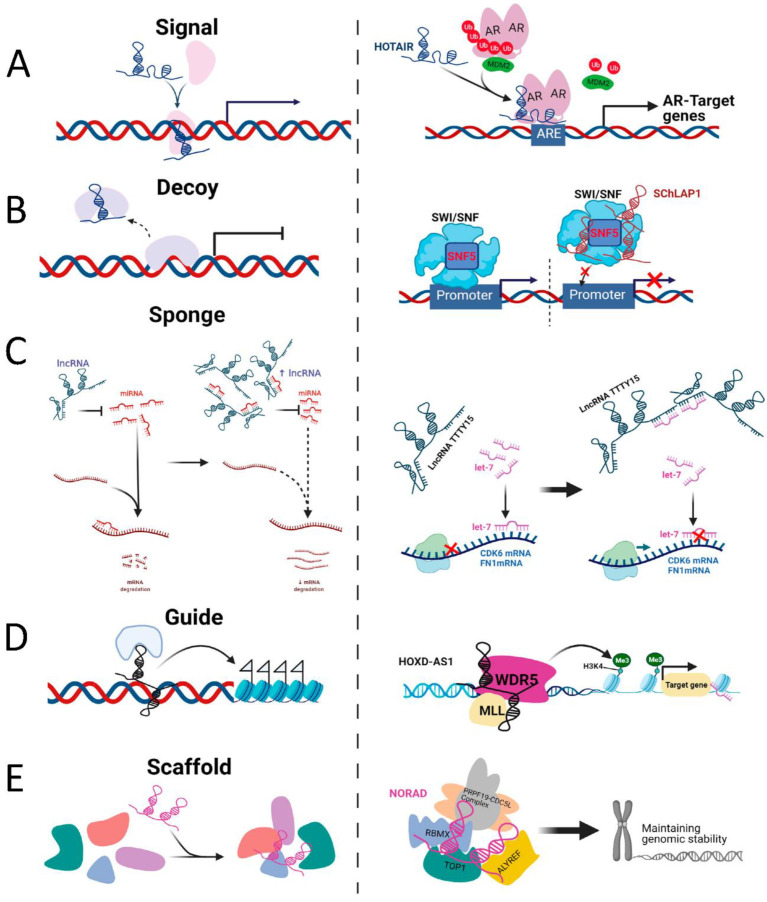
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the molecular mechanisms of four lncRNA archetypes and their examples. (A) as signals, lncRNAs regulate transcriptional activity or gene expression (e.g., lncRNA HOTAIR). (B) as decoys, lncRNAs can bind transcription factors or regulatory proteins and displace them from DNA binding sites (e.g., lncRNA SChLAP1). (C) as sponges, lncRNAs can function as miRNA sponges and compete for miRNA binding to its target mRNA expression (e.g., lncRNA TTTY15). (D) as guides, lncRNA can recruit or relocalise regulation factors to activate or repress gene expression either in “cis” or “trans”. (e.g., lncRNA HOXD-AS1). (E) as scaffolds, lncRNAs can act as adaptors, bringing binding partner proteins within close proximity to aid the formation of Ribonucleoprotein complexes (e.g., lncRNA NORAD).