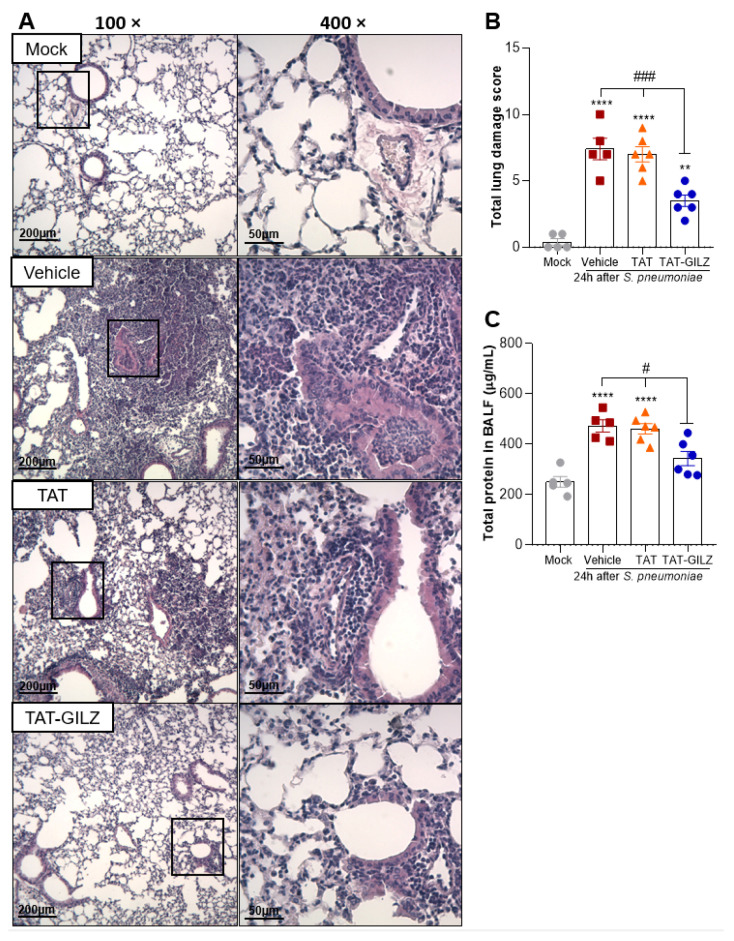
Figure 5.
Effect of treatment with TAT-GILZ in lung damage caused by pneumococcal infection. BALB/c mice were infected with S. pneumoniae (1 × 105 CFU, i.n.), and then treated with TAT (0.1 mg/kg, i.p.) or TAT-GILZ (0.2 mg/kg, i.p.) 12 h p.i., and euthanized 24 h p.i. Mock group (uninfected) received salina and vehicle group received DMSO 0.6%. Representative slides of hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stained lungs are shown (A). Scale bars = 200 µm (low magnification) and 50 µm (high magnification). Right slides are higher magnifications (400×) of the selected areas (boxes) in left slides (100×). Histopathological score evaluated airway, vascular, and parenchymal inflammation, neutrophilic infiltration, and epithelial injury (B). The total protein level in BAL is show in (C). Data are mean ± SEM of N = 5–6 animals per group. ** p < 0.01, **** p < 0.0001 when compared to mock group, or as indicated: # p < 0.05, ### p < 0.001 when comparing TAT-GILZ-treated pneumococcal pneumonia mice to vehicle or TAT groups, by 1-way ANOVA.