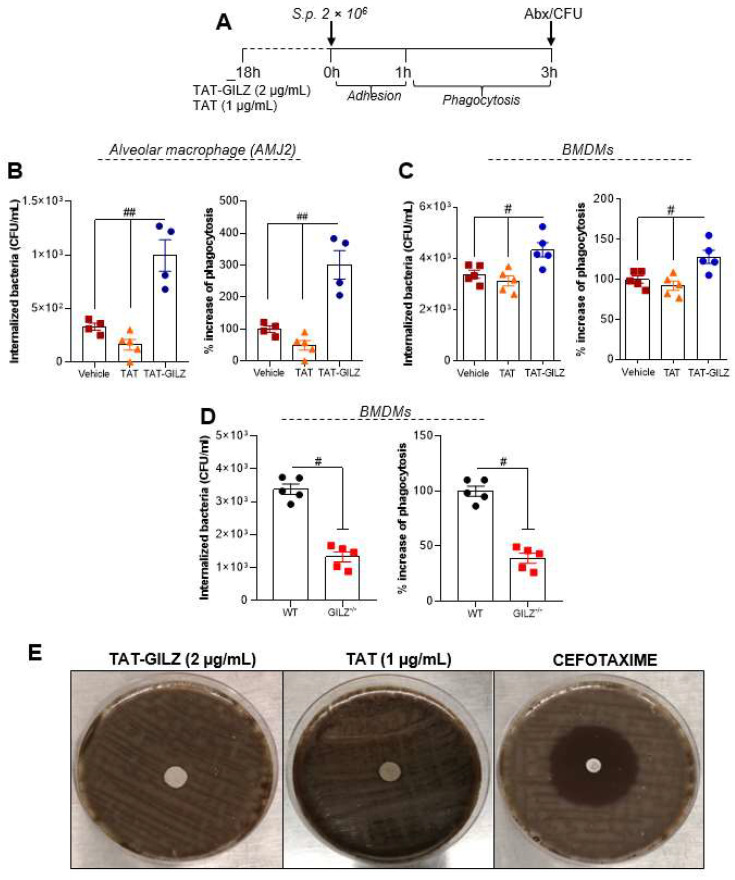
Figure 6.
TAT-GILZ enhanced macrophages phagocytosis of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Phagocytosis of bacteria–Experimental design in (A)–were evaluated in alveolar macrophages (AMJ2-C11) (B) or BMDMs obtained from WT mice (C). Macrophages (2 × 105) were pre-treated with TAT (1 μg/mL) or TAT-GILZ (2 μg/mL) for 18 h and then incubated with S. pneumoniae (MOI 1:10) for 3 h to allow adhesion and phagocytosis. Noninternalized bacteria were excluded by the incubation of the cells with penicillin/streptomycin (Abx), followed by the lysis of macrophages to identify the number of viable phagocytosed bacteria. In other experimental group BMDMs from naïve WT and GILZ−/− (2 × 105) were also subjected to phagocytosis as describe bellow (D). Results are expressed as CFU of internalized bacteria or % of phagocytosis (CFU counts on blood agar plates, N = 4–5) and are presented as mean ± SEM; # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01 when comparing TAT-GILZ-treated cells to vehicle or TAT, by 1-way ANOVA (B–C). Comparison between BMDMs from WT and GILZ−/− were by t-test (# p < 0.05). Data are representative of 3 independent experiments performed in biological quadruplicates or quintuplicates. TAT-GILZ (2 μg/mL), TAT (1 μg/mL) or cefotaxime (30 μg—control) impregnated on sterile filters were then added to blood agar plates containing S. pneumoniae. The Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) only defines MIC values for cephalosporins. However, here we have performed the disc diffusion method using a cefotaxime disc for comparative purposes. The zone of growth inhibition was evaluated after 18 h incubation at 37 °C and 5% CO2 (E).