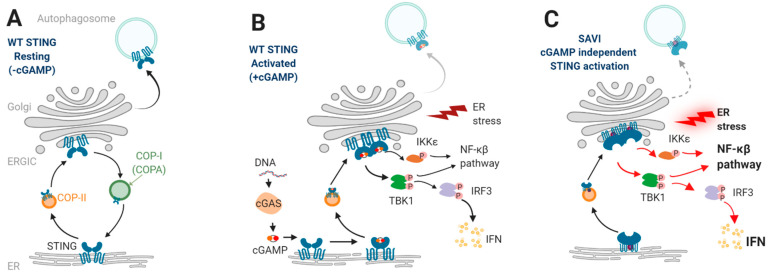
Figure 1.
STING Signaling. (A,B) Upon DNA sensing by cGAS, cGAMP binds to wild-type (WT) STING. STING trafficks then to the Golgi and undergoes post-translational modifications. STING activation in the Golgi leads to type I interferon (IFN) production, NF-κβ pathway activation, and cell death induction through endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. STING trafficking is normally controlled through retro-transport to the ER via COPA and by trafficking to the autophagosome, where it is degraded. (C) When affected by a gain-of-function mutation, STING is constitutively activated in the Golgi in a cGAMP-independent manner and enhances constitutive type I IFN production through IRF3 phosphorylation and inflammatory cytokine production by activating the NF-κβ pathway. STING constitutive activation in the Golgi also induces ER stress, which can further lead to cell death. Finally, reduction of STING clearance by autophagy is described in the context of STING gain-of-function. Adapted from Frémond et al., J Clin Immunol, 2021. Created with biorender.com, accessed on 26 November 2021, last accessed on 13 January 2022.