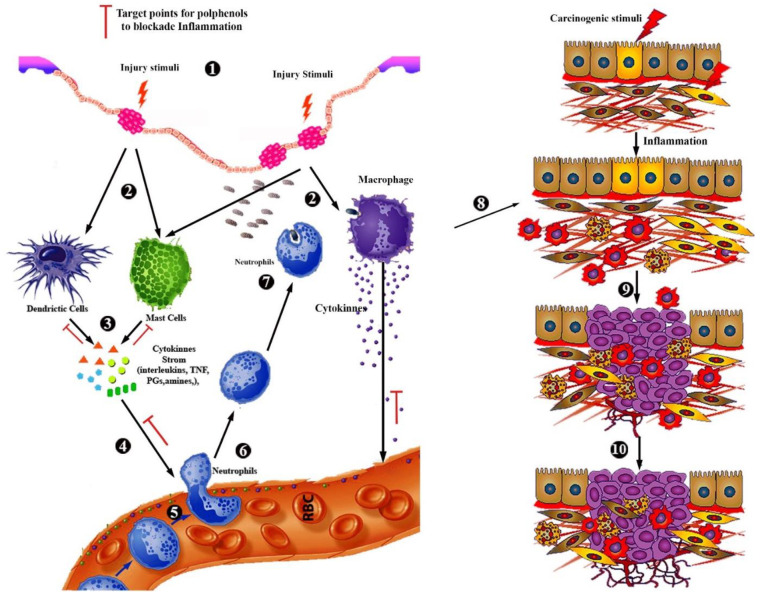
Scheme 1.
Mechanism of inflammation leading to carcinogenicity (signed by the authors Saeed Akhtar and Muqeet Wahid using Adobe). 1. Carcinogenic or injury stimuli cause the injury on the epithelium layer of tissue. 2. Activation of dendritic, mast cells, and macrophages present under epithelium layer in between parenchymal cells of the tissue. 3. Dendritic, mast cells, and macrophages release the proinflammatory cytokines (TNF, interleukins, PGs, amines, amines, etc.). 4. Cytokines act on blood vessels for vasoconstriction to migrate platelets and neutrophils from blood vessels to the site of inflammation. 5. Neutrophils roll and 6. Migrate to the site of inflammation. 7. Neutrophils engulf the microbes and necrotic cells. 8. Chronic inflammation may lead to the mutagenicity and proliferation of cells 9. Inflammation and mutagenicity lead to the uncontrolled proliferation of cells with hyperplasia and dysplasia. 10. Angiogenesis with uncontrolled proliferation of cells, which leads to tumor formation in tissue.