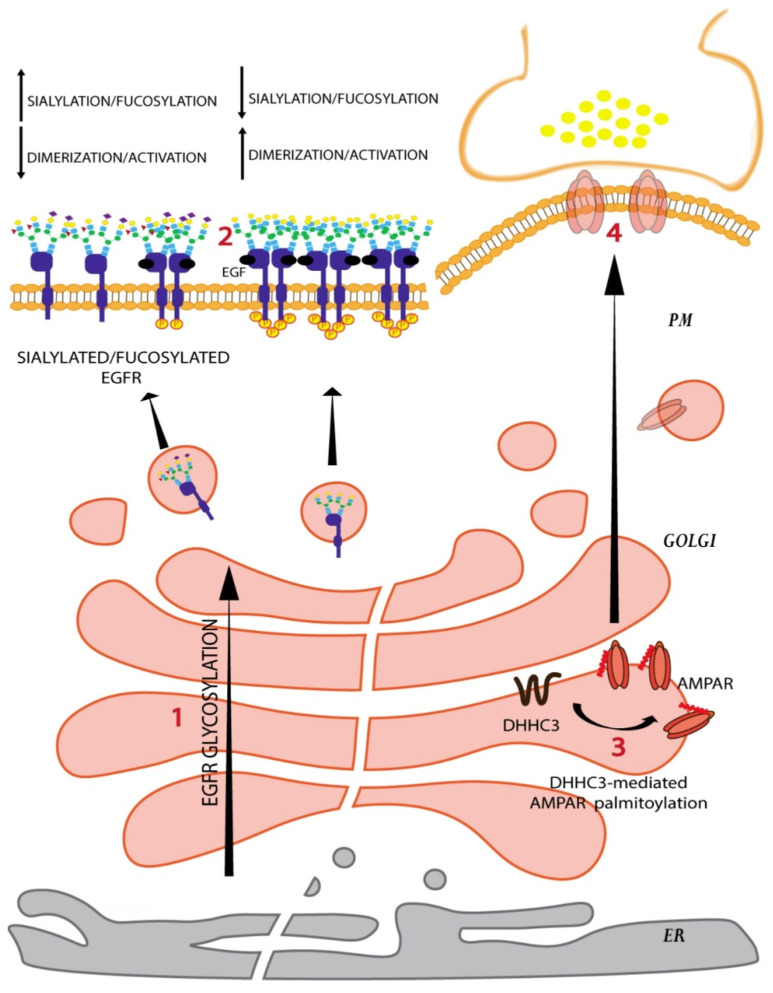
Figure 4.
Golgi glycosylation and palmitoylation affect protein localization and function processing reactions in the Golgi,= determine the sialylation and fucosylation levels of EGFR. Increased sialylation or fucosylation reduces EGFR dimerization and activation (1) while reduced sialylation or fucosyaltion promotes it (2). The glutamate-gated ion channels AMPARs are made by different combinations of four subunits, GLUA1-4, each of which is palmitoylated. Palmitoylation of GLUA1 and GLUA2 is mediated by the Golgi resident palmitoyltransferase DHHC3 (3) and causes AMPAR retention in the Golgi and reduction of its expression at PM (4). This in turn impacts synaptic plasticity.