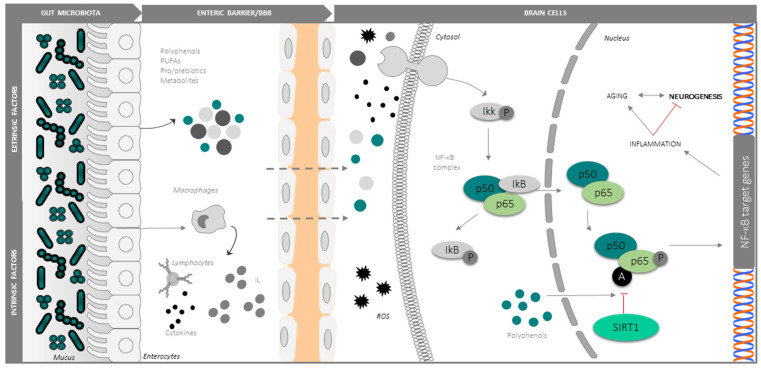
Figure 3.
Central role of the SIRT1-NF-kB signalling pathway in neuroinflammation and its modulation by dietary, microbial and immune factors from the intestine. Cytokines, bacterial wall components and ROS activate NF-kB, while polyphenols inhibit proinflammatory signalling via SIRT-1 mediated inhibitory deacetylation of the factor. Both enteric and BBB act as microbe-modifiable checkpoints in the intestine-gut communication. See the text for details.