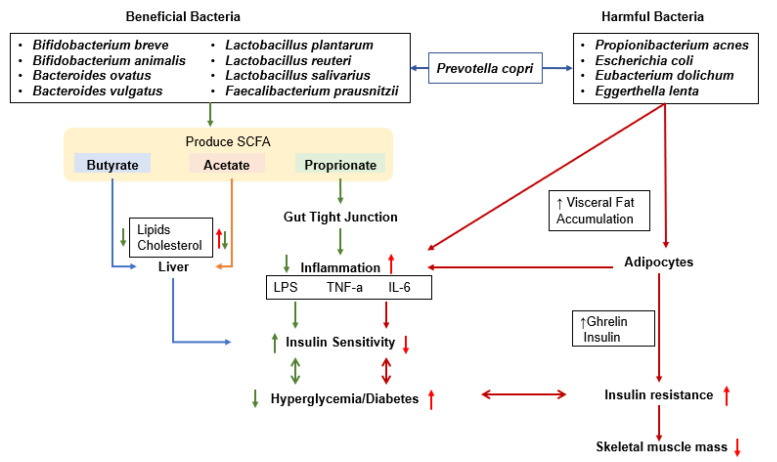
Figure 2.
Proposed interaction of gut bacteria with glucose metabolism. Effects of gut microbiota and their products on the liver, gut cell wall, adipocytes, and inflammation as regulators of glucose metabolism are explained; gut bacteria can increase and decrease inflammation, either improving or exacerbating insulin resistance and muscle loss. LPS, lipopolysaccharide; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; IL-6, interleukin-6.