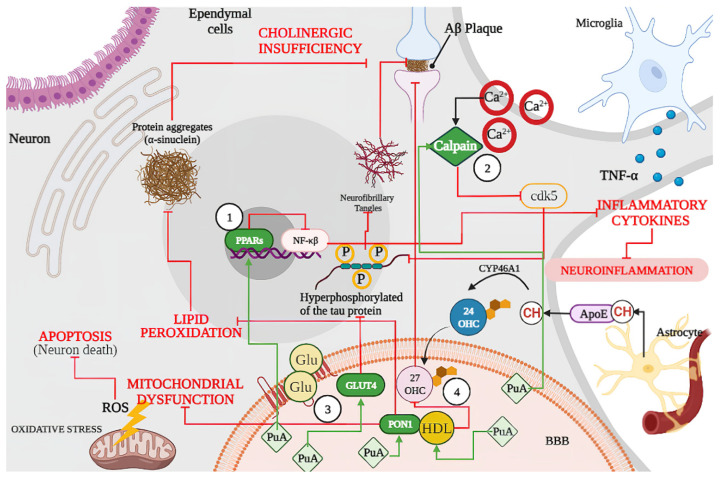
Figure 6.
Schematic representation of biological effects of punicic acid (PuA) in neurological diseases (NDs). Punicic acid (PuA) acts as (1) an agonist of PPARs inhibiting the activation of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) and the release of inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-alpha, and therefore, reducing neuroinflammation and tau hyperphosphorylation and conducting less Aβ formation and aggregation. (2) PuA inhibits activation of calpain and cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (cdk5), limiting the hyperphosphorylation of tau protein and conducting to less Aβ formation and aggregation. (3) PuA increases GLUT4 protein expression regulating the glucose brain metabolism, reducing insulin resistance, and reducing the hyperphosphorylation of tau proteins. (4) PuA increased the anti-oxidative properties of the PON1 complex reducing ROS generation limiting mitochondrial dysfunction and neuronal apoptosis. Lipids peroxidation. Moreover, PuA induces changes in high-density lipoproteins (HDL) lipid composition and functionality reducing the formation of oxysterols such as 27-hydroxycholesterol (27-OHC) and increasing oxidative resistance with less Aβ plaque formation. ROS: reactive oxygen species; PON1: paraoxonase 1; PPARs: peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors; HDL: high-density lipoprotein; GLUT4: insulin-sensitive glucose transporter; CH: cholesterol; BBB: blood–brain barrier; ApoE: apolipoprotein E; Glu: glucose, PuA: punicic acid. Green lines indicate stimulation, while red lines indicate inhibition.