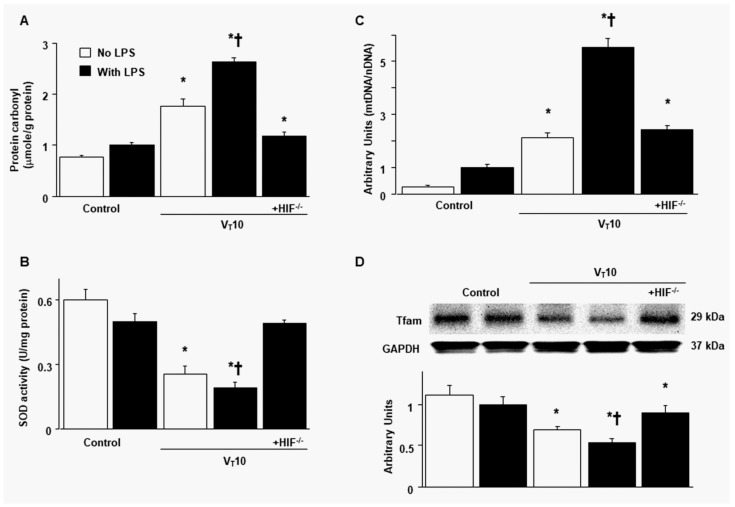
Figure 2.
Inhibition of endotoxin-augmented mechanical ventilation-induced oxidative load, mitochondrial DNA, and mitochondrial transcription factor A in HIF-1α-deficient mice. (A) Protein carbonyl groups and (B) SOD were from the diaphragms of nonventilated control mice and mice ventilated at a tidal volume of 10 mL/kg for 8 h with or without LPS administration (n = 5 per group). (C) Real-time PCR performed for mitochondrial DNA expression was from the diaphragms of nonventilated control mice and mice ventilated at a tidal volume of 10 mL/kg for 8 h with or without LPS administration (n = 5 per group). Arbitrary units were expressed as the ratio of mitochondrial DNA to nuclear DNA (n = 5 per group). (D) Western blots were performed using antibodies that recognize mitochondrial transcription factor A and GAPDH expression from the diaphragms of nonventilated control mice and mice ventilated at a tidal volume of 10 mL/kg for 8 h with or without LPS administration (n = 5 per group). Arbitrary units were expressed as relative Tfam activation (n = 5 per group). * p < 0.05 versus the nonventilated control mice with LPS treatment; † p < 0.05 versus all other groups. GAPDH = glyceraldehydes-phosphate dehydrogenase; mt = mitochondria; nDNA = nuclear DNA; SOD = superoxide dismutase; Tfam = mitochondrial transcription factor A.