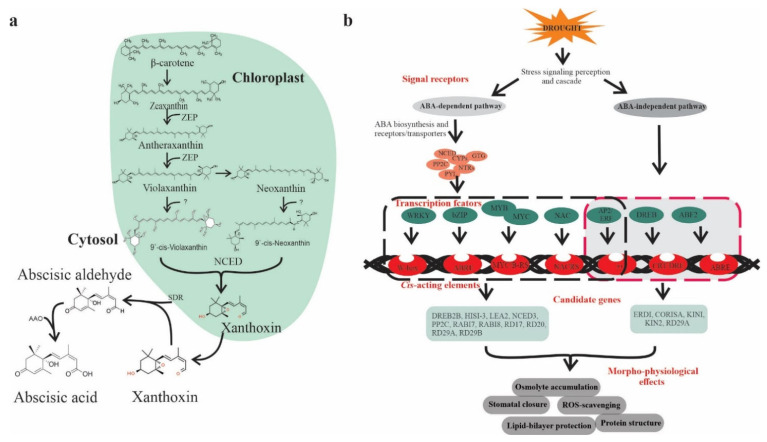
Figure 1.
ABA biosynthesis and ABA-mediated drought-responsive pathways in plants. (a) Scheme of ABA biosynthesis. The precursors of ABA, β-carotene undergoes a series of oxidative reactions in the plastids and each step is catalyzed by specific enzyme such as ZEP (zeaxanthin epoxidase) or NCED (9-cis-epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase). The derived xanthoxin is exported to the cytosol and converted into ABA through an oxidation reaction mediated by AAO (aldehyde oxidase) and SDR (alcohol dehydrogenase/reductase), (b) ABA-dependent and -independent signaling pathways in the plant, which consists of several core components including ABA receptors and regulators. The ABA-dependent and -independent pathways are indicated by black and red arrows, respectively. Transcription factors (TFs) include bZIPs, MYB/MYC2, NAC (RD26), and WRKY bind to their corresponding cis-acting elements W-box, ABRE, MYB, MYC, DREB2, AREB/ABF, and NACRs.