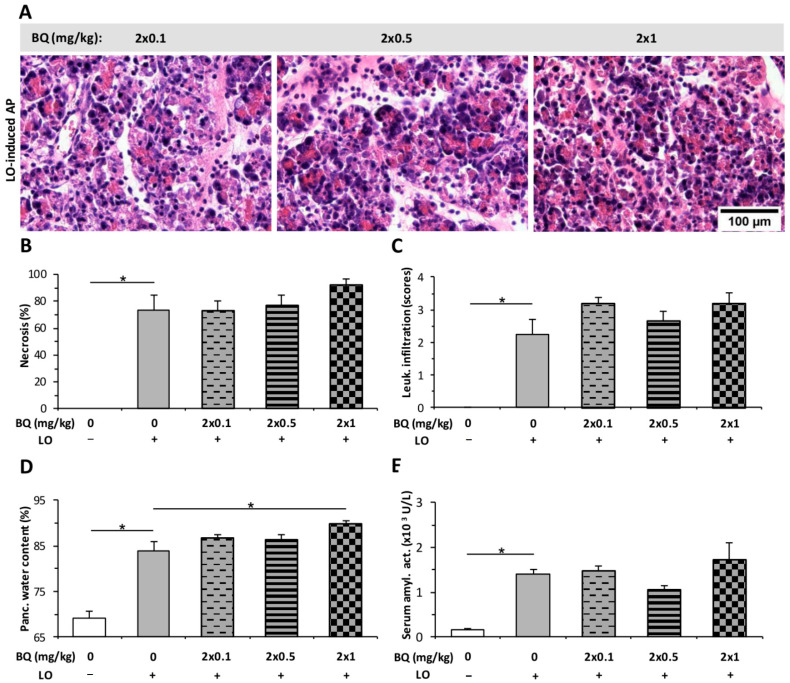
Figure 8.
Intraperitoneal (i.p.) buprenorphine (BQ) treatment does not affect the severity of L-ornithine (LO)-induced acute pancreatitis (AP). Rats were treated with 2 × 0.1, 2 × 0.5, or 2 × 1 mg/kg BQ i.p., whereas i.p. injection with 3 g/kg LO (LO +) was used to induce AP. Control animals received physiological saline instead of LO (LO −) or BQ (0 mg/kg). Animals were sacrificed at 24 h after the first CER or physiological saline injection. (A) Representative histopathological images of pancreatic tissues of the treatment groups. Bar charts show the extent of pancreatic (B) necrosis, (C) leukocyte infiltration, (D) water content, and (E) serum amylase activity measurements. Values represent mean with standard error, n = 6. Two-way ANOVA was performed followed by the Holm–Sidak post hoc test. * p < 0.05.