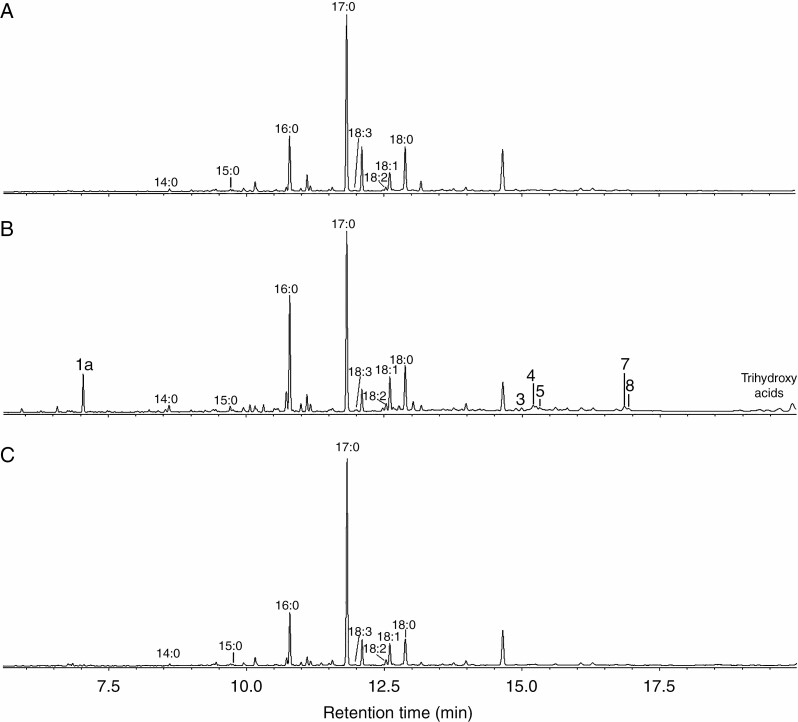
Fig. 5.
The total ion current GC-MS chromatograms of endogenous oxylipins (Me/TMS with preliminary NaBH4 reduction) of intact plants (A) and plants infected with the wild-type Pectobacterium atrosepticum (typical infection) (B) or coronafacic acid-deficient P. atrosepticum mutant (latent infection) (C). 1a, 9-Hydroxynonanoic acid (NaBH4-reduced 9-oxononanoic acid, 9-HPL product); 3, colneleic acid (9-DES product); 4, 9-HOD (derivative of 9-LOX product); 5, 9-HOT (derivative of 9-LOX product); 7, 9,10-epoxy-11-hydroxy-12-octadecenoic acid (9-EAS product); 8, 9,10-epoxy-11-hydroxy-12,15-octadecadienoic acid (9-EAS product). 14:0, myristic acid; 15:0, pentadecanoic acid; 16:0, palmitic acid; 17:0, margaric acid (internal standard); 18:0, octadecanoic acid; 18:1, octadecenoic acid; 18:2, linoleic acid; 18:3, α-linolenic acid. Trihydroxy acids are products of epoxyalcohol hydrolysis. Extraction, derivatization and analysis procedures are described in the Materials and Methods. The structural formulae of the revealed oxylipins are presented in Fig. 3.