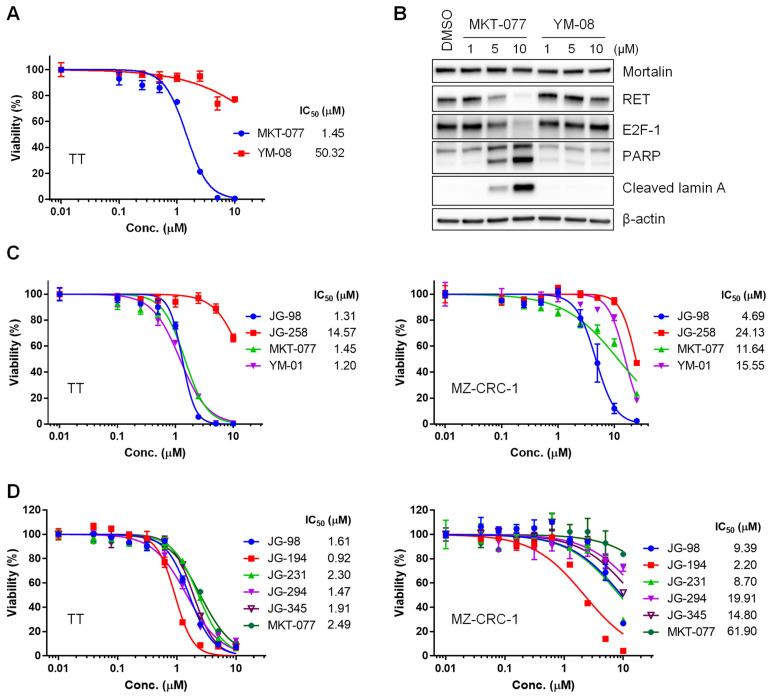
Figure 1.
Effects of MKT-077 derivatives in TT and MZ-CRC-1 cells. (A) TT cells in 24-well plates were treated with serially increasing doses of MKT-077 and YM-08 for 48 h. Cells were then allowed to recover in drug-free fresh medium for 48 h, prior to determining cell viability by MTT assay, as described in the Materials and Methods. Data (mean ± SEM, n = 3) are expressed as the percentage of vehicle-treated control. The IC50 values were calculated by PRISM. (B) Western blot analysis of total lysates of TT cells treated with MKT-077 and YM-08 for 48 h. β-actin is the control for equal protein loading. Equal volume of DMSO was used as the vehicle control. Blots are representative of two independent experiments. (C) IC50 analysis in TT and MZ-CRC-1 cell cultures treated with indicated inhibitors for 72 h. Cell viability was determined by MTT assay. Data (mean ± SEM, n = 3) are expressed as the percentage of vehicle-treated control. (D) IC50 analysis in TT and MZ-CRC-1 cell cultures treated with indicated inhibitors for 72 h. Cell viability was determined by MTT assay. Data (mean ± SEM, n = 3) are expressed as the percentage of vehicle-treated control. 95% Confidence Intervals in TT were 1.474 to 1.772 (JG-98), 0.848 to 1.019 (JG-194), 2.095 to 2.541 (JG-231), 1.315 to 1.653 (JG-294), 1.785 to 2.052 (JG-345), and 2.261 to 2.758 (MKT-077). While, 95% Confidence Intervals in MZ-CRC-1 were 6.070 to 14.54 (JG-98), 1.592 to 3.047 (JG-194), 5.917 to 12.80 (JG-231), 14.11 to 28.09 (JG-294), 10.92 to 20.06 (JG-345), and 29.85 to 128.4 (MKT-077).