Table 1.
Different methods for M-NPs synthesis.
| Method | Graphical Representation | Short Description | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Top-Down synthesis | Mechanical Milling |
|
This approach includes the disintegration of particle aggregates, particle shape, and particle surface. | [20,21,22,23] |
| Chemical Etching |
|
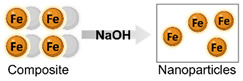
Uses a strong acid or a corrosive liquid to cut a metal surface and create a design in the metal. | [24,25] | |
| Sputtering |
|
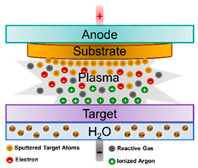
There is a particular sputtering technique called magnetron sputtering, which consists of the delivery of a high voltage across a low-pressure gas (normally argon) to create a plasma of high energy composed of electrons and gas ions, which will strike a target containing the desired coating material. | [26,27] | |
| Laser Ablation |
|
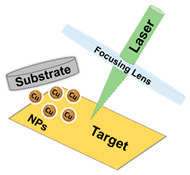
Is based on the production of micropatterns through the ablation (removal) of fractions of a substrate through the action of a focused pulsed laser beam. | [20,28] | |
| Electro Explosion |
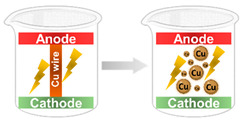
|
Single-step process in which a delicate wire of a conductive metal is exploded by an electric discharge that is caused by a high-power DC source. This electronic discharge creates a massive temperature that vaporizes the thin wire, turning it into gas atoms, which in their turn are chilled and, finally, the NPs are synthesized. | [29,30] | |
| Bottom-up synthesis | Chemical Deposition |
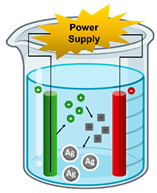
|
In particular, electrochemical deposition or electrochemical precipitation involves the passage of an electric current between an anode (sacrificial) and a cathode localized in an electrolyte. The anode is oxidized into metal ions and these are then reduced to metal by the cathode with the help of stabilizers. | [31,32] |
| Spinning |
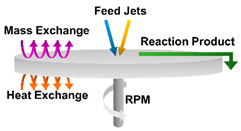
|
This method involves the use of a spinning disc reactor. The disc spins at different speeds and the spinning causes the fusion and precipitation of atoms, which are then collected. | [5,33] | |
| Sol–Gel |
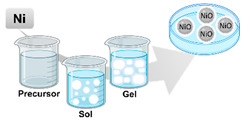
|
A wet-chemical process, with sol being a colloidal solution of solids suspended in a liquid phase that serves as a metal precursor and is then dispersed into the gel, a host liquid leading to the formation of a solid macromolecule submerged in the solvent. After, there is a separate phase where the gel is dried and dehydrated to recover the NPs. | [20,24,33,34,35] | |
| Biosynthesis |
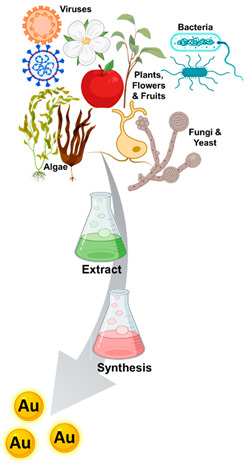
|
Metalsynthesis is bio-mediated by microbes or through biosynthesis. Biological synthesis of nanomaterials is the best alternative being cost-effective, environmentally friendly, advantageous and does not comprise any input of toxic chemicals. Between the candidates to biosynthesize M-NPs are bacteria, fungi and yeast; algae; plants, flowers and fruits; and viruses. | [18,19,23,36,37,38] |
