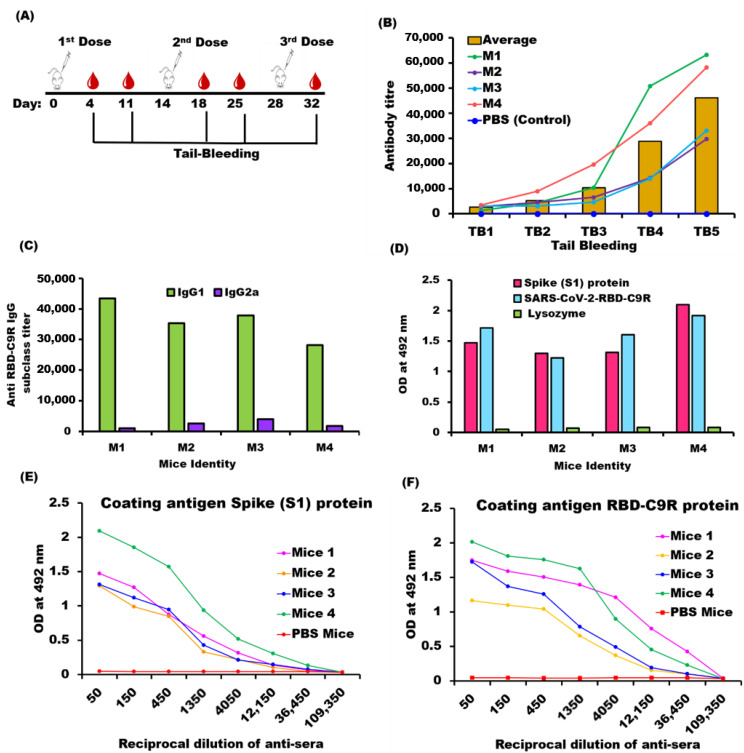
Figure 4.
Immunogenicity of RBD-C9R. (A) Immunization scheme: A group of four mice was immunized with 0.3 mg/mL of RBD-C9R in 10 mM tris buffer without adjuvant. Up to three doses were injected biweekly, and tail bleed (TB) samples were collected three days after injection for monitoring the IgG titer by ELISA. M-indicates the mice’s identity, and TB indicates the tail bleeding number (once a week). (B) RBD-C9R IgG titer: IgG detection by ELISA was performed using the tail bleeding (TB) sera. Each circle indicates the individual mice titer, and the bars show the average titer (calculated over all four mice). (C) IgG sub-class (IgG1, IgG2a) Determination: Tail bleeding 5 (TB-5) serum sample was used for ELISA. (D) Recognition of mammalian expressed spike protein by RBD-C9R antisera: The binding of TB5 serum was measured using mammalian expressed spike (S1) protein as coating antigen and RBD-C9R as coating antigen for comparison. The plates were titrated using the mice antisera raised against RBD-C9R. The binding specificity of the antisera was determined with plates coated with lysozyme, as a control. The bar symbols are explained within the panel. (E) Absorbance at 492 nm vs. the reciprocal of antisera dilution against native Spike (S1) protein. (F) Absorbance at 492 nm vs. the reciprocal of antisera dilution against RBD-C9R (legends are given in the panel).