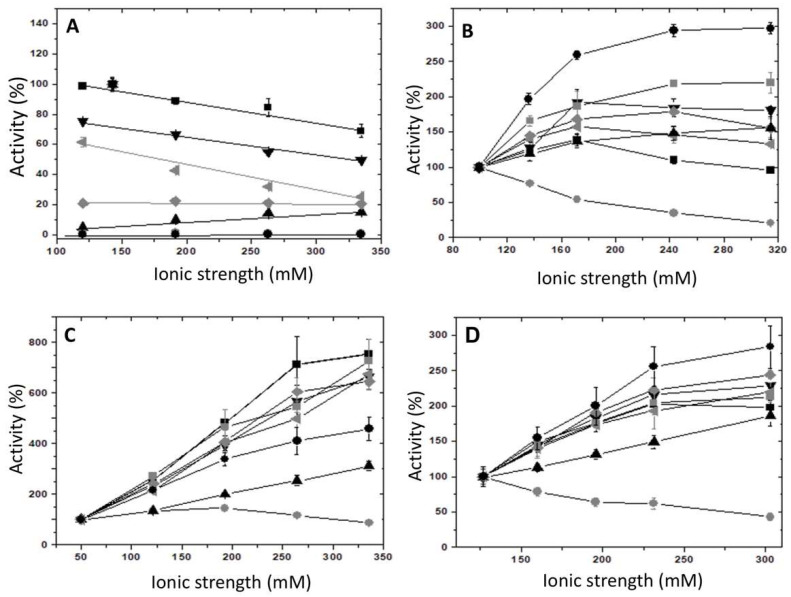
Figure 2.
Effect of ionic strength on the activities of WT-RMPK (A), E117K (B), T113L/E117K (C), and T113L/K114Q/E117K (D) mutants induced by the indicated monovalent cations. In the absence of monovalent cations, the reaction mixtures contained ionic strengths of 99.5, 50, and 126.8 mM in (B–D), respectively. The activities in these conditions for (B–D) were 14 ± 3, 10 ± 1 and 34 ± 4, respectively. In the presence of 90 mM K+, the activity for (A) was 263 ± 15 and ionic strength 143 mM. These activities were normalized to 100%, which corresponded to the control activity for each PK. Besides 25 mM HEPES-(CH3)4NOH pH 7.4, 0.2 mM NADH, 8 μg/ml LDH and a reaction mixture with saturating concentrations of substrates, Li+ (●), Na+ (▲), K+ (∎), NH4+ (◀), Rb+ (▼), Cs+ (♦), choline (●) or (CH3)4N+ (∎) were added to complete the ionic strengths indicated in the figure. Reaction mixtures contained: (A) 0.64 mM PEP3−, 2.5 mM Mg-ADP, 1.69 mM Mg2+free; (B) 0.63 mM PEP3−, 2 mM Mg-ADP and 19 mM Mg2+free; (C) 0.54 mM PEP3−, 0.7 mM Mg-ADP and 3 mM Mg2+free and (D) 0.67 mM PEP3−, 1.84 mM Mg-ADP and 24 mM Mg2+free. Assays were performed at 25 °C, and the reaction was started by the addition of PK. Amounts of PK ranged from 0.1 to 0.2 μg/mL. Standard deviation bars of three experiments are shown.