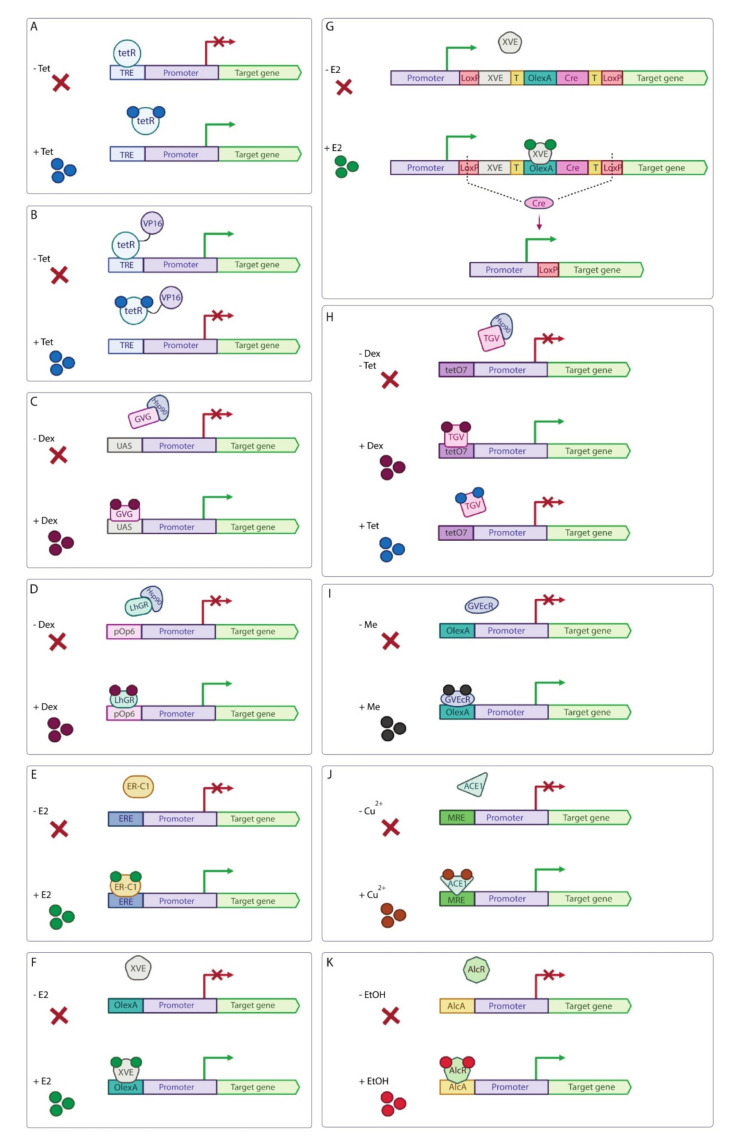
Figure 6.
Schematic representation of chemically-inducible systems for regulation of transgene expression in plants. (A) The Tet-derepressible system. In the absence of tetracycline (Tet), tetR binds to TRE sequences, and the target gene is not transcribed. Upon Tet addition, tetR cannot bind to TRE, allowing the target gene transcription. (B) The Tet-off system. In the absence of Tet, tetR-VP16 binds to TRE resulting in activation of the target gene. In the presence of Tet, tetR-VP16 cannot bind to TRE to induce the transgene expression. (C) The GVG/UAS system. In the absence of dexamethasone (Dex), GVG binds to the regulatory protein Hsp90 forming an inactive complex. Dex addition results in the dissociation of GVG from the Hsp90 protein and its binding to UAS upstream of the target gene. (D) The pOp6/LhGR system. In the absence of Dex, LhGR binds to the regulatory protein Hsp90, and, thus, is inactive. In the presence of Dex, LhGR binds to pOp6 sequence to activate the transgene expression. (E) ER-C1 system. In the absence of β-estradiol (E2), ER-C1 does not bind to ER elements (ERE). Once activated by E2, ER-C1 binds to ERE and activates target gene expression. (F) The XVE system. In the absence of E2, XVE does not bind to the LexA operator sequence (OlexA). After treatment with E2, XVE binds to OlexA and activates the target gene expression. (G) The XVE-controlled Cre/loxP system. The XVE and Cre expression cassettes are located between the constitutive promoter and the target gene flanked by two loxP sites. In uninduced condition, the target gene is not expressed. In the presence of inducer (E2), XVE activates the Cre transcription, resulting in the fusion of the constitutive promoter and the target gene due to Cre/loxP-mediated recombination. T—transcription terminator. (H) A dual-controlled TGV system. In the absence of Dex and Tet, TGV binds to the Hsp90 protein, forming an inactive complex. Upon Dex addition, TGV separates from Hsp90, binds to the Tet operator sequence (tetO7) and activates the target gene expression. In the presence of Tet, the TGV protein dissociates from the reporter gene promoter and the level of the target gene transcription drops to uninduced levels. (I) The GVEcR system. Without methoxyfenozide (Me), GVEcR does not bind to the LexA binding site (OlexA) and the target gene is not transcribed. In the presence of Me, GVEcR binds to OlexA and activates the target gene transcription. (J) The copper-inducible system. In the absence of copper (Cu2+), the transcription factor ACE1 does not bind to metal responsive element (MRE) and the transgene is not transcribed. In the presence of copper ions, ACE1 binds to MRE and activates the target gene transcription. (K) The ethanol-inducible system. Without ethanol (EtOH), the transcription factor AlcR does not bind to the promoter of the AlcA gene (AlcA) and the transgene is not transcribed. After addition of ethanol, AlcR binds to AlcA and activates the transgene expression.