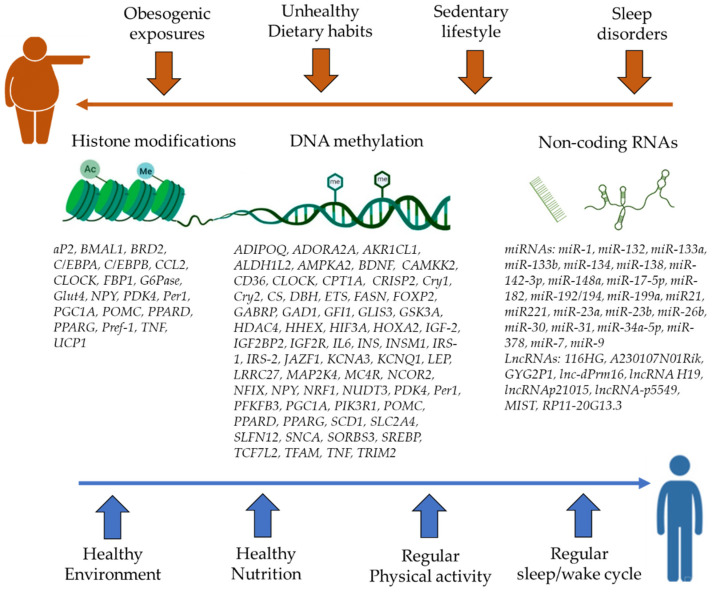
Figure 1.
Epigenetic regulations of genes related to obesity. An illustration of the most prevalent epigenetic modifications and targeted genes researched in the context of obesogenic versus healthy lifestyle choices. ADIPOQ (adiponectin), ADORA2A (adenosine A2a receptor), AKR1CL1 (aldo-keto reductase family 1 member C8), ALDH1L2 (aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 family member L2), AMPKA2 (AMP-activated, alpha 2 catalytic subunit), aP2 (adipocyte protein 2), BDNF (brain-derived neurotrophic factor), BMAL1 (brain and muscle aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator–like 1), BRD2 (bromodomain containing 2), C/EBPA (CCAAT enhancer binding protein alpha), C/EBPB (CCAAT enhancer binding protein beta), CAMKK2 (calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase 2), CCL2 (C-C motif chemokine ligand 2), CLOCK (circadian locomotor output cycles kaput), CPT1A (carnitine palmitoyl transferase 1A), CRISP2 (cysteine rich secretory protein 2), Cry1 (cryptochrome circadian regulator 1), Cry2 (cryptochrome circadian regulator 2), CS (citrate synthase), DBH (dopamine beta-hydroxylase), ETS (E-twenty-six transcription factor), FASN (fatty acid synthase), FBP1 (fructose-bisphosphatase 1), FOXP2 (forkhead box P2), G6Pase (glucose-6-phosphatase), GABRP (gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptor subunit pi), GAD1 (glutamate decarboxylase 1), GFI1 (growth factor independent 1 transcriptional repressor), GLIS3 (GLIS family zinc finger 3), GLUT4 (glucose transporter 4), GSK3A (glycogen synthase kinase 3 alpha), GYG2P1 (glycogenin 2 pseudogene 1), HDAC4 (histone deacetylase 4), HHEX (hematopoietically expressed homeobox), HIF3A (hypoxia-inducible factor 3 subunit alpha), HOXA2 (homeobox A2), IGF-2 (insulin-like growth factor 2), IGF2BP2 (insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 2), IGF2R (insulin-like growth factor 2 receptor), IL6 (interleukin 6), INS (insulin), INSM1 (insulinoma-associated 1), IRS-1 (insulin receptor 1), IRS-2 (insulin receptor 2), JAZF1 (Juxtaposed with another zinc finger protein 1), KCNA3 (potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily A member 3), KCNQ1 (potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily Q member 1), LEP (leptin), LRRC27 (leucine-rich repeat containing 27), MAP2K4 (mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 4), MC4R (melanocortin 4 receptor), MIST (Macrophage Inflammation-Suppressing Transcript), NCOR2 (nuclear receptor corepressor 2), NFIX (nuclear factor I X), NPY (neuropeptide Y), NRF1 (nuclear respiratory factor 1), NUDT3 (nudix hydrolase 3), PDK4 (pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4), Per1 (period circadian regulator 1), PFKFB3 (6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-biphosphatase 3), PGC1A (PPARG coactivator 1 alpha), PIK3R1 (phosphoinositide-3-kinase regulatory subunit 1), POMC (proopiomelanocortin), PPARD (peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta), PPARG (peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma), Pref-1 (DLK1; delta like non-canonical Notch ligand 1), SCD1 (stearoyl-coenzyme A desaturase 1), SLC2A4 (solute carrier family 2 member 4), SLFN12 (schlafen family member 12), SNCA (synuclein alpha), SORBS3 (sorbin and SH3 domain containing 3), SREBP (Sterol regulatory element binding protein), TCF7L2 (transcription factor 7 like 2), TFAM (transcription factor A, mitochondrial), TNF (tumor necrosis factor), TRIM2 (tripartite motif containing 2), UCP1 (uncoupling protein 1).