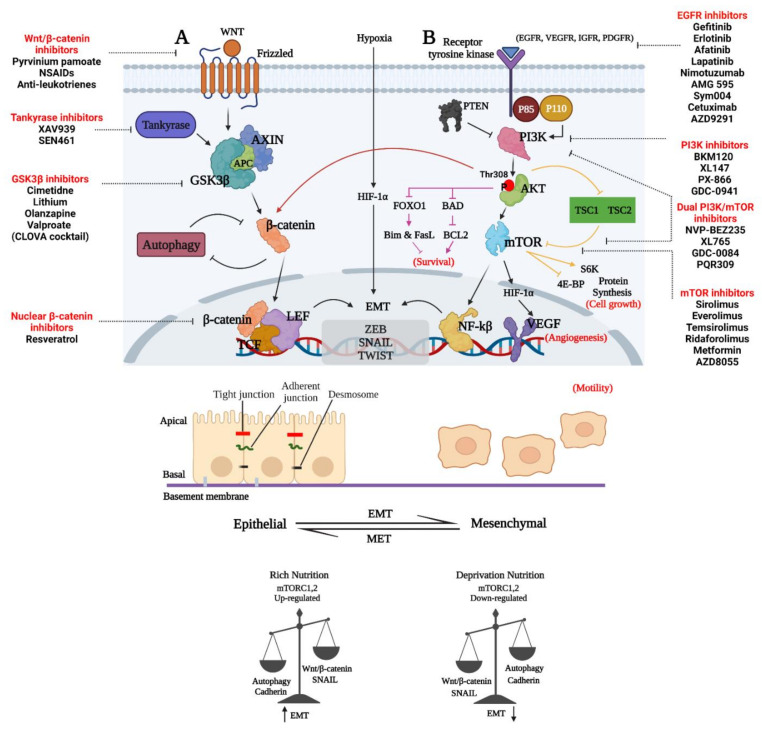
Figure 3.
Representative image of GBM invasion through the regulation of the interconnected Wnt/β-catenin, PAM, and EMT signaling pathways. (A) Disheveled protein (DVL) enhances the phosphorylation of LRP5/6 co-receptor and the recruitment of axin to the membrane. DVL is recruited in the presence of WNT ligands (WNT1, WINT3A and WNT8) bound to FZD. Non-phosphorylated β-catenin may enter the nucleus when the destruction complex is dissociated to form a complex with the TCF/LEF proteins [124]. (B) PI3K regulator (p85) and catalytic isoform (p110) are released from inhibition when growth factors interact with their cognate RTK, resulting in the activation of PI3K. An inhibitor of PTEN may prevent PIP2 synthesis from PIP3, a process catalyzed by PI3K. The PH domain of Akt is then recruited to the plasma membrane by PIP3 and forms an Akt-PIP3 complex. To alleviate the inhibitory effect of TSC1-TSC2 on mTORC1, Akt phosphorylates and inhibits TSC2. Prolonged tumor cell survival, proliferation, migration, invasion, and glucose metabolism are all promoted by activated Akt phosphorylation of downstream system components. The Akt–mTORC1 axis also influences protein synthesis and cell proliferation. An additional negative feedback loop is created when the mTORC1 pathway is activated [122]. Abbreviations: APC, adenomatous polyposis coli; CK1α, casein kinase 1α; GSK3β, glycogen synthase kinase 3β; LRP5/6, low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5/6; β-TREP, beta-transducing repeat-containing protein; TCF/LEF, T-cell factor/lymphoid enhancer-binding factor; TSC1, TSC Complex Subunit 1; 4E-BP, 4E-binding protein 1; FOXO1, forkhead box O1; S6K, ribosomal protein S6 kinase; PDGFR, platelet-derived growth factor receptor; IGFR, insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor. (Created with https://biorender.com/, accessed on 25 July 2021).