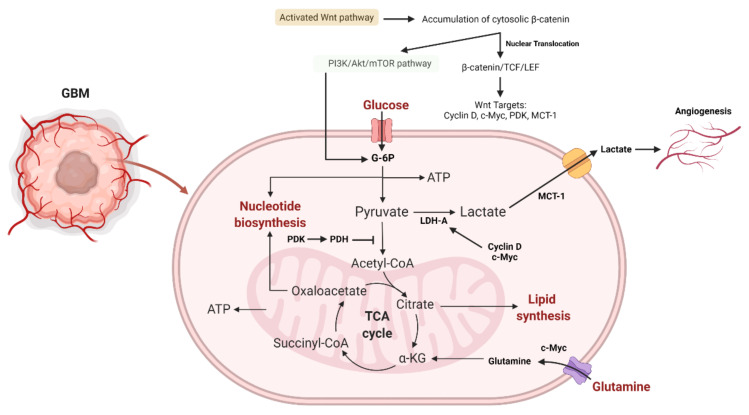
Figure 5.
The role of the Wnt and PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathways in glioma aerobic glycolysis. The association of β-catenin to TCF-LEF results in the transcription of Wnt-sensitive genes (PDK, c-Myc, cyclin D, MCT-1). MCT-1 promotes lactate extrusion from the cytosol, hence promoting angiogenesis. Activating PI3K/Akt results in an increase in glucose metabolism. By activating HIF-1α, which inhibits glucose entry into the TCA cycle, Akt-transformed cells defend against ROS damage. HIF-1α-induced PDK1 phosphorylates PDH, culminating in the conversion of cytosolic pyruvate to lactate through the activation of LDH-A. Because PDK inhibits the PDH complex in the mitochondria, pyruvate cannot be converted completely to acetyl-CoA and enter the TCA cycle. Additionally, c-Myc and cyclin D activate LDH-A, which catalyzes the conversion of cytosolic pyruvate to lactate. c-Myc facilitates the entrance of glutamine into the cytosol and mitochondria. Glutamate generated by c-Myc promotes aspartate and nucleotide synthesis [229]. Abbreviations: PDK, pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase; MCT-1, monocarboxylate transporter 1, ROS, reactive oxygen species; PDH, pyruvate dehydrogenase; LDH-A, lactate dehydrogenase A (created with https://biorender.com/, accessed on 28 December 2021).