Figure 23.
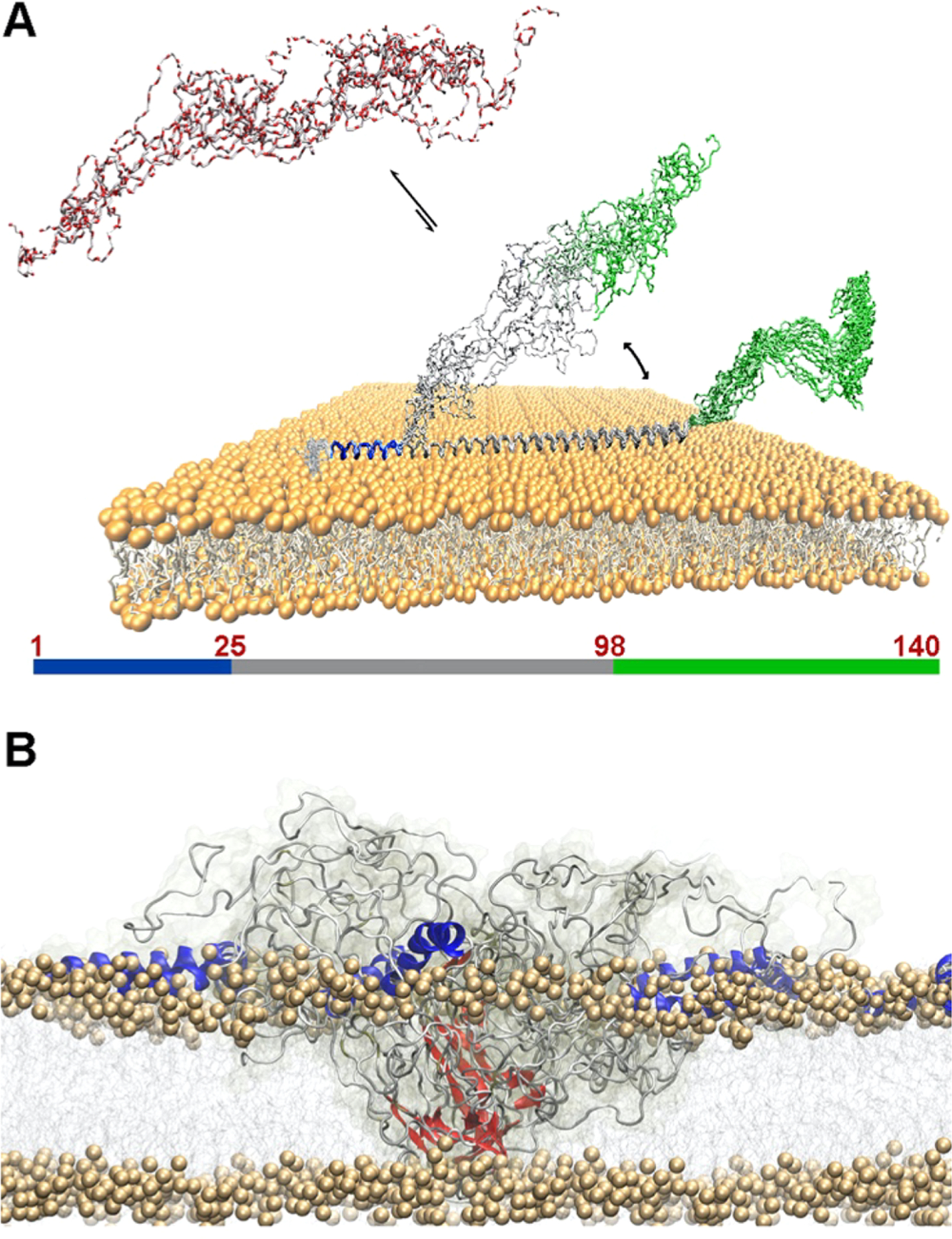
Membrane binding by monomeric and oligomeric αS. (A) Monomeric αS is disordered in solution (red) and binds the membrane with three regions having distinct structural and dynamical properties. The N-terminal region (blue) acts as a rigid membrane anchor. The central region (gray) is in conformational exchange between membrane-bound (helical) and detached (disordered) conformations. The C-terminal region (green) remains essentially unbound from the membrane.299 (B) The membrane binding by toxic αS oligomers involves N-terminal regions (blue) of αS molecules from the oligomer, strongly anchoring the oligomers to the membrane surface in a cooperative manner, and the prefibrilar β-sheeted rigid core (red), inserting into the lipid bilayer and disrupting its integrity.650
