Figure 26.
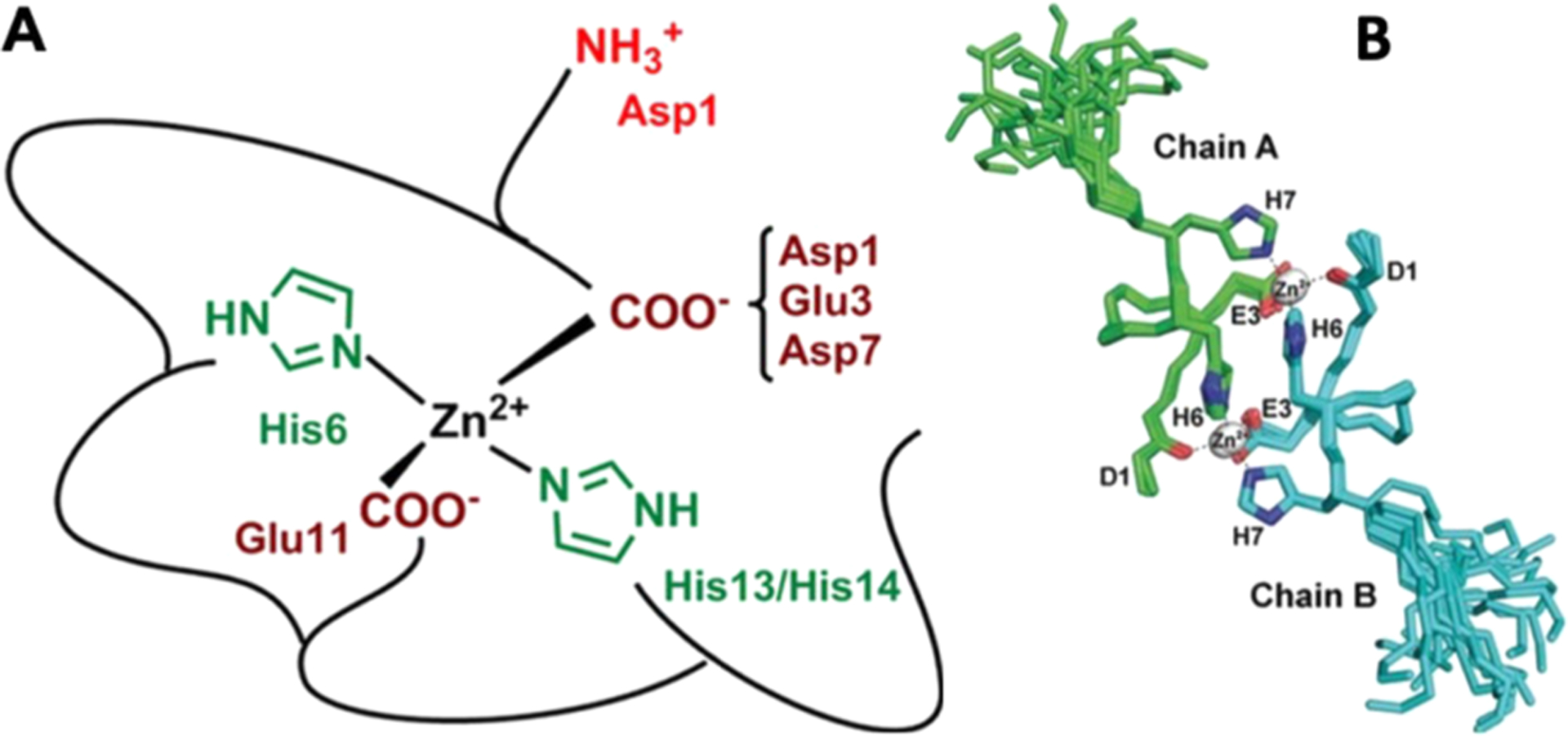
High-resolution structural characterization of zinc binding sites to Alzheimer’s Aβ. (A) At physiological pH (7.4), zinc was proposed to tetrahedrally bind with Aβ where the coordination sphere is contributed from two of three histidine (H6, H13, and H14) residues and two carboxylate side chains (E11 and one from D1, E3, or D7). (B) Superimposition of 20 NMR model structures of Taiwanese mutant Aβ fragment (D7H-Aβ1–10) showing zinc (gray sphere) induced formation of a homodimer. The dimer is stabilized by two zinc ions where one coordinates to D1 and H6 of one Aβ subunit and the other to H7 and E3 orienting the H6 residue of both subunits to form stacking interactions.695,700
