Figure 5.
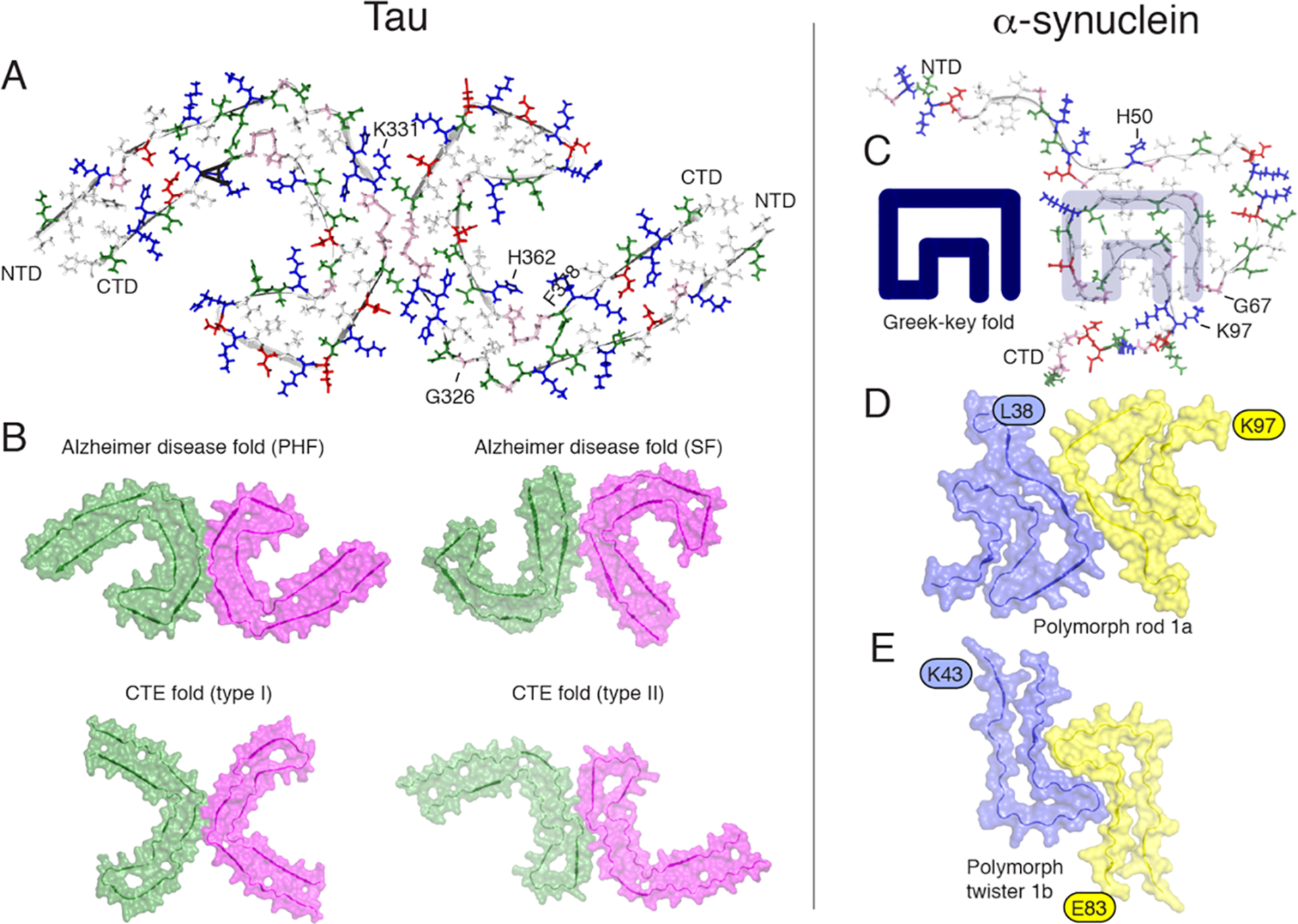
Orthogonal view of the three-dimensional structural models of tau filaments and α-synuclein amyloid fibrils. NTD and CTD are the N-terminal and C-terminal domains. (A) Solid-state tau paired PHF spanning residues 306–378 in the right protofilament. (B) Cryo-EM PHF and SF tau amyloid cores in AD. In chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE), tau filaments contain predominantly the type I (90%) and type II filaments. The interprotofilament interfaces are different compared to those in AD. (C) Amyloid core of human α-synuclein amyloid fibrils (PDB 2NOA), containing a Greek-key fold. (D and E) Amyloid core fibril structure of α-synuclein: polymorph rod 1a (PDB entry 6CU7) and polymorph twister 1b (PDB entry 6CU8). The authors prepared the figure with pymol.254
