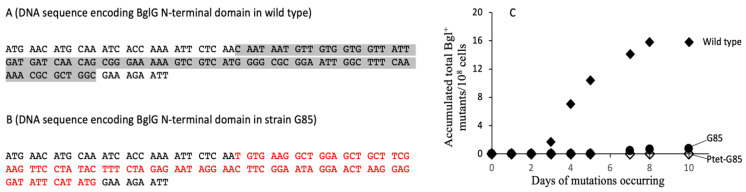
Figure 5.
N-terminal domain of BglG is required for enhancement of Bgl+ mutations. (A) DNA sequence of the portion of bglG encoding BglG’s N-terminal domain in the wild type protein. (B) DNA sequence of the portion of bglG corresponding to the altered N-terminal domain of BglG in strain G85. The 85-bp DNA region in grey (A) that encodes 28 N-terminal residues of BglG was replaced by an 85-bp DNA scar (red-faced nucleotides) in (B). This 85-bp scar is in frame within the bglG gene and has no stop codon. (C) Bgl+ mutation assays using strain G85 without or with bglG overexpression. Strains G85 (with the altered 28 residues at N-terminal residues of the native BglG) and Ptet-G85 (with the intact bglG in native bgl operon plus Ptet driving bglG85 at the intS locus of BW25115) were subject to Bgl+ mutation assays as described in the legend to Figure 1 and the Section 4. Solid diamonds: wild type bglG; solid circles: G85; open diamonds: Ptet-G85.