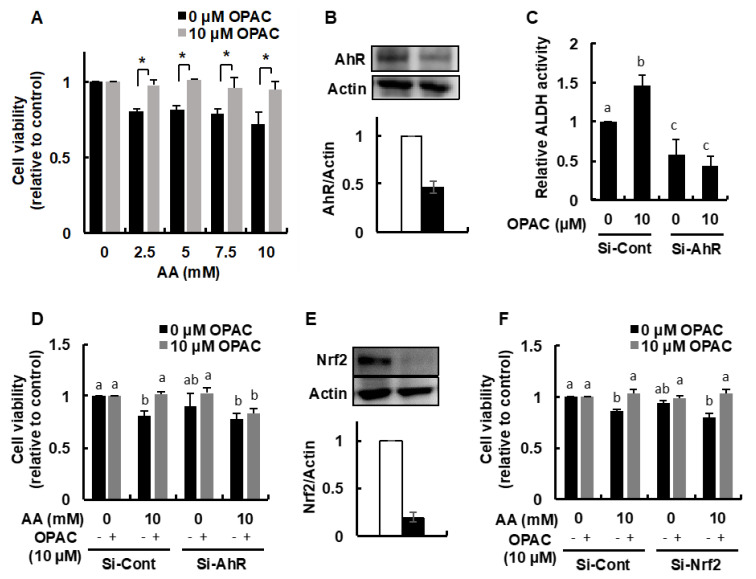
Figure 5.
AhR-dependent protection against the acetaldehyde-induced cytotoxicity by OPAC. (A) Inhibitory effect of OPAC pretreatment on the acetaldehyde-induced cytotoxicity. After Hepa1c1c7 cells were pretreated with OPAC for 6 h, the cells were treated with different concentrations of acetaldehyde for 3 h; then, an MTT assay was carried out. (B) Modulating effect of AhR siRNA on the AhR protein level in the whole cell lysates. Hepa1c1c7 cells were transfected with the AhR siRNA or control scrambled siRNA, then incubated for 48 h. The total cell lysates were subjected to a Western blot analysis (n = 2). (C) Modulating effect of AhR siRNA on the total ALDH activity. The Hepa1c1c7 cells transfected with the AhR siRNA or control scrambled siRNA were treated with OPAC for 6 h, and the total ALDH activity was determined by a microplate reader (340 nm). (D) Impairment of the OPAC-enhanced resistance to the acetaldehyde-induced cytotoxicity by the AhR siRNA. After the Hepa1c1c7 cells transfected with siRNA were pretreated with OPAC for 6 h, the cells were treated with different concentrations of acetaldehyde for 3 h; then, an MTT assay was carried out. (E) Modulating effect of Nrf2 siRNA on the Nrf2 protein level in the whole cell lysates. Hepa1c1c7 cells were transfected with the Nrf2 siRNA or control scrambled siRNA, then incubated for 48 h. The total cell lysates were subjected to a Western blot analysis (n = 2). (F) No significant effect of the Nrf2 siRNA on the OPAC-enhanced resistance to the acetaldehyde-induced cytotoxicity. All values are expressed as means ± SD of three separate experiments and analyzed by a Student’s t-test or a one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey’s HSD using XLSTAT software. The different letters above the bars indicate significant differences among the treatments for each condition (* p < 0.05 vs. control).