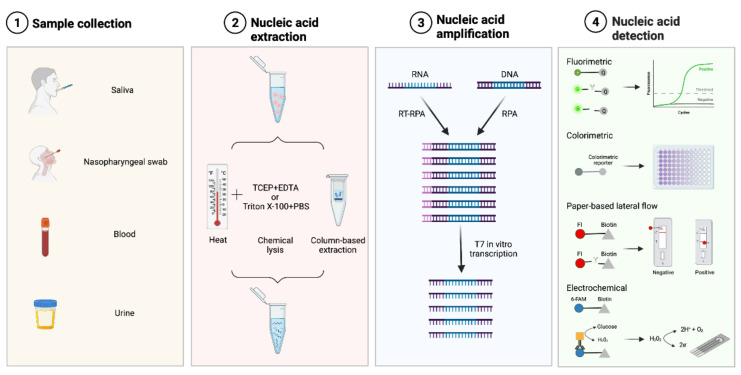
Figure 3.
Schematic of the steps required for Cas13-based diagnostics. 1. Sample can be collected from saliva, nasopharyngeal secretions, blood or urine. 2. Nucleic acids are extracted using different methods depending on the diagnostic tool. Heat and chemical lysis are combined for a quick extraction; column-based is used for standard extraction. 3. Nucleic acids can be amplified by different isothermal amplification protocols such as recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA) in DNA samples, or reverse transcription RPA (RT-RPA) in RNA samples, followed by in vitro T7 transcription of the amplified product into RNA. 4. The activation of the Cas13 enzyme is produced after the binding of the crRNA to the complementary target sequence, triggering collateral cleavage of fluorometric, colorimetric, biotin, or electrochemical reporters.