Figure 2: Schematic of grid and FIB/SEM geometry.
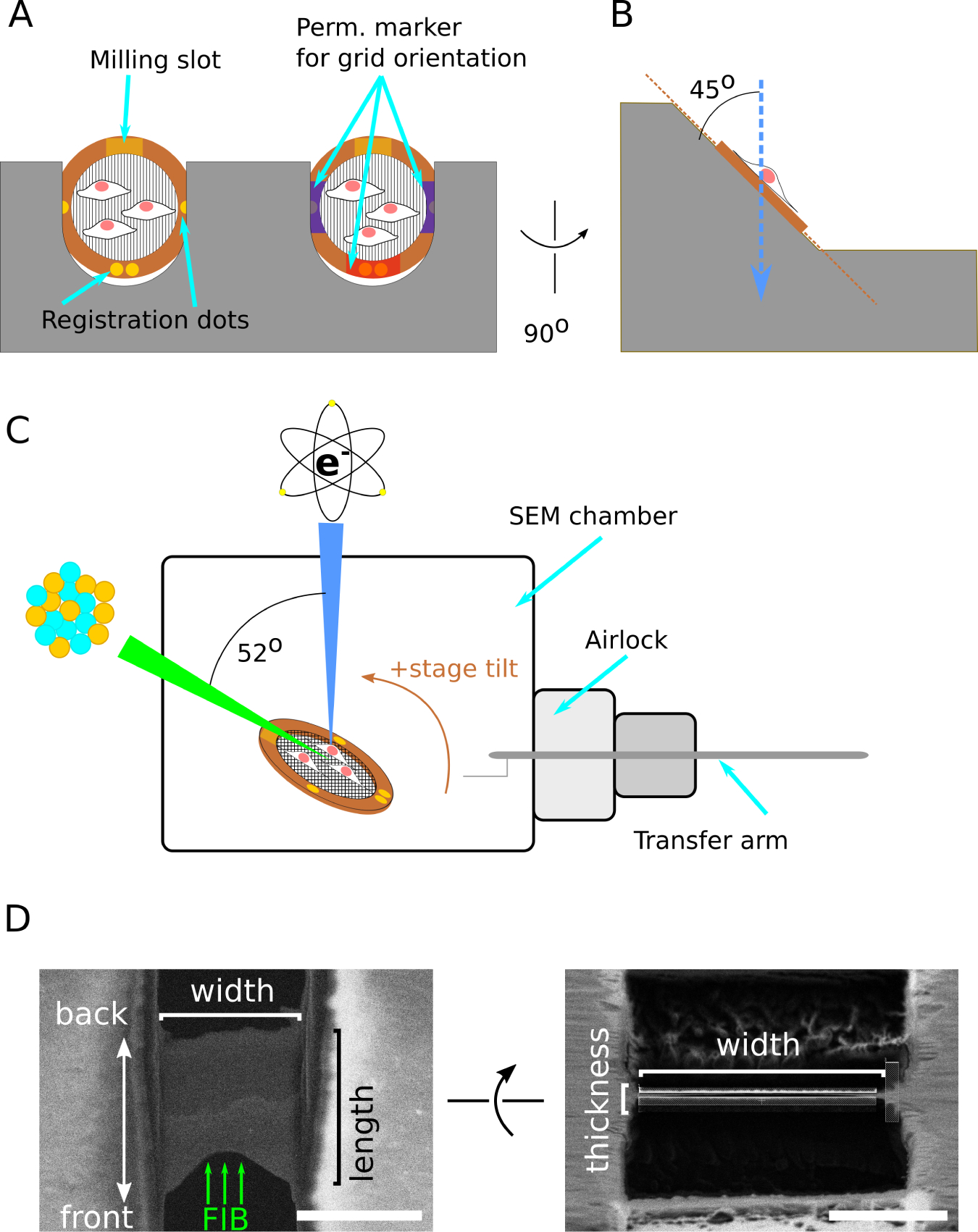
(A) Schematic of two grids clipped into an cryo-FIB-autogrid support and loaded into the shuttle, with cells on the top surface. The cryo-FIB-autogrid has a milling slot that enables lower angle milling and registration dots for aligning the grid when loading at the SEM or TEM. Additional markings with permanent marker can be made to enhance visibility under liquid nitrogen. Compare to Fig. 3E. (B) Side view of grid loaded into shuttle, illustrating the grids are held at a 45° angle relative to vertical. (C) Schematic of relative orientation of the SEM column, FIB column, sample stage, and transfer arm. The grid is positioned at the beam-coincident point, and the milling slot is oriented toward the FIB column. The stage is arranged to have positive tilt towards the FIB column. This results in FIB-sample incident angle 7° smaller than the reported stage angle. SEM beam is indicated in blue, FIB in green, and the specimen in copper. (D) Schematic of terminology used in this chapter to refer to lamella dimensions and orientation. Scale bars: 5 μm
