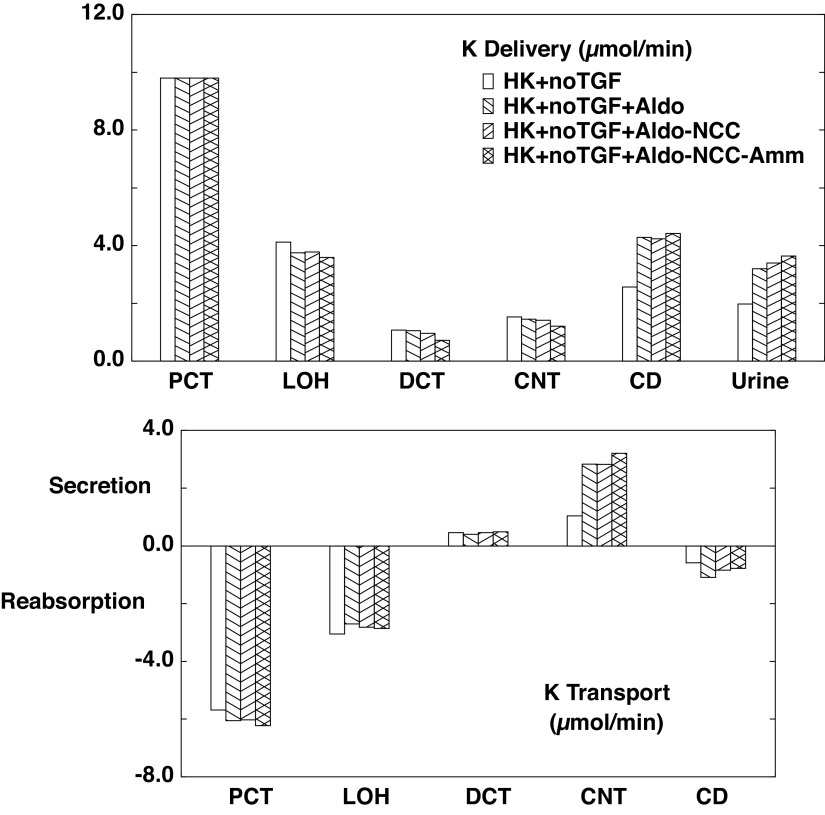
Figure 9.
Segmental accounting of whole kidney K+ flows (delivery) and fluxes (transport), in hyperkalemia, with tubuloglomerular feedback (TGF) fixed at its normokalemic value (A1). Negative or positive transport values correspond to reabsorptive or secretory fluxes. As in Fig. 8, open bars denote unregulated hyperkalemia (HK + no TGF; A3); backslash bars indicate aldosterone (Aldo) action, a doubling of the density of the epithelial Na+ channel and Na+-K+-ATPase in principal cells (HK + no TGF + Aldo; C1); forward slash bars adds an 80% reduction in NaCl cotransporter density (HK + no TGF + Aldo-NCC; C2); and cross-hatched bars add a halving of ammoniagenesis (HK + no TGF + Aldo-NCC-Amm; C3). The values shown are those in Table 9. Because of the higher glomerular filtration rate, there are higher distal flows, so that the Aldo action to augment K+ excretion is most prominent; the other regulatory responses are less potent. CD, collecting duct; CNT, connecting tubule; DCT, distal convoluted tubule; LOH, loop of Henle; PCT, proximal convoluted tubule.