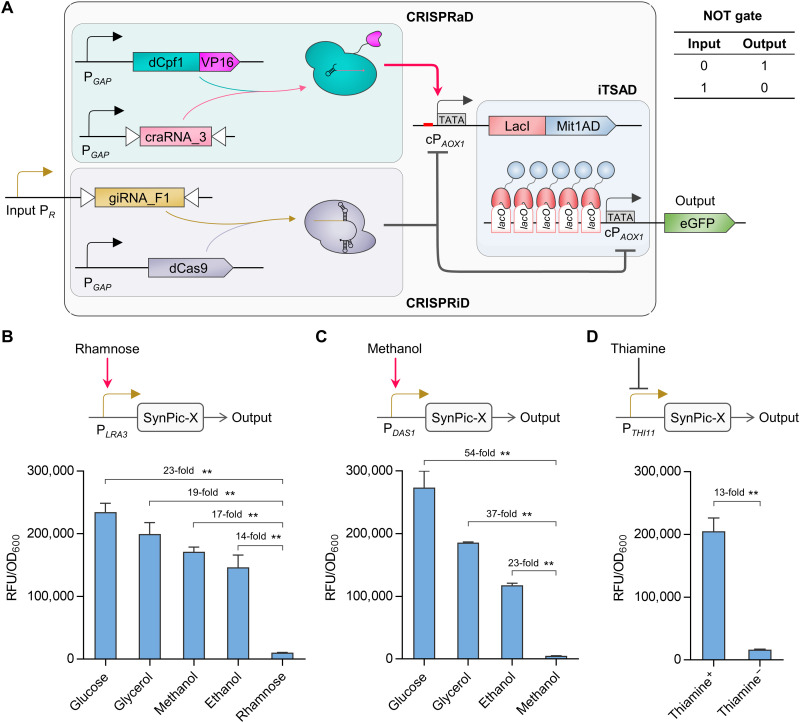
Fig. 6. Development of the synthetic P. pastoris system (SynPic) responsive to defined signals.
(A) Overview of the SynPic-X platform. CRISPRaD mediated by dCpf1-VP16/craRNA_3, CRISPRiD mediated by dCas9/giRNA_F1, and iTSAD were used to set up the SynPic-X platform. A relatively strong promoter PGAP was used to constitutively drive dCpf1-VP16/craRNA_3 in CRISPRaD and dCas9 in CRISPRiD. The input promoter PR was used to drive giRNA_F1 in CRISPRiD. The whole genetic circuit logic of the SynPic-X platform conforms to a logic NOT gate. (B) SynPic-R system derived from SynPic-X with input promoter PLRA3. P. pastoris endogenous rhamnose-inducible promoter, PLRA3, was selected as PR to construct a rhamnose-responsive switch. The output of SynPic-R was repressed with rhamnose but activated with glucose (23-fold), glycerol (19-fold), methanol (17-fold), and ethanol (14-fold). (C) SynPic-M system derived from SynPic-X with input promoter PDAS1. P. pastoris endogenous methanol-inducible promoter, PDAS1, was selected as PR to produce a methanol-responsive switch, which was repressed with methanol but activated with glucose (54-fold), glycerol (37-fold), and ethanol (23-fold). (D) SynPic-T system derived from SynPic-X with input promoter PTHI11. P. pastoris endogenous promoter, PTHI11, which is repressed by thiamine, was used to construct a thiamine-responsive switch. The SynPic-T remained OFF in the absence of thiamine but turned ON after thiamine was added (13-fold). Statistical significance of eGFP expression of each strain in specific carbon sources is shown (**P < 0.01). RFU, relative fluorescence unit.