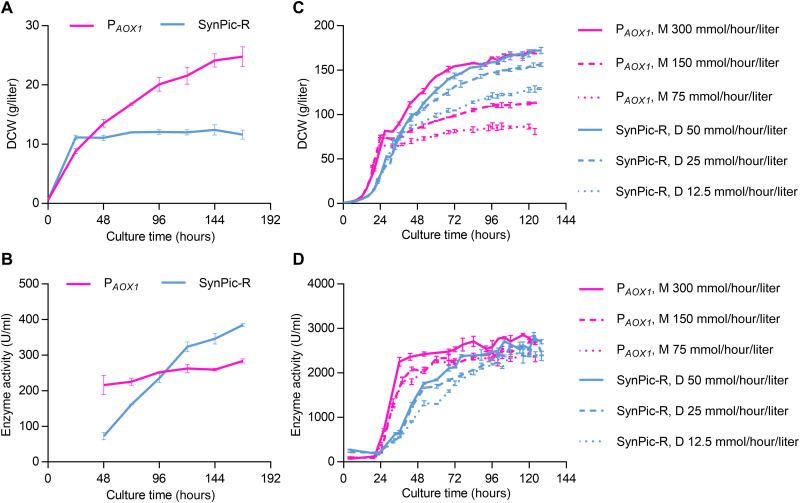
Fig. 7. Comparison of α-amylase production driven by PAOX1 and SynPic-R.
(A) Growth and (B) enzyme activity of yeast strains expressing α-amylase by GS115/PAOX1 or SynPic-R in shake flasks. Methanol and glucose were used as the sole carbon source to induce GS115/PAOX1 and SynPic-R, respectively. (C) Growth and (D) enzyme activity of yeast strains expressing α-amylase by GS115/PAOX1 or SynPic-R in 3-liter bioreactors fermented under different feeding rates. For α-amylase expression by PAOX1, the fermentation strategy included a glycerol-fed batch phase and a methanol (M) induction phase. For α-amylase expression by SynPic-R, the fermentation strategy included a rhamnose-fed batch phase and a glucose (D) induction phase. The yeast strains were grown in the basal salt medium with glycerol or rhamnose feeding to a dry cell weight of about 67 g/liter and then were switched to the induction phase. Three different feeding rates of methanol and glucose were used with consistent carbon content in the induction phase. Broth samples were collected every 24 hours in a shake flask and every 4 to 8 hours in a bioreactor. Error bars at some time points are small and covered by the time curves. Detailed medium and culture methods are described in Materials and Methods. DCW, dry cell weight.